Since its imposition in 2018, the value-added tax in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia has become an integral part of the country’s tax and economic system. This tax is considered a vital pivot in generating revenues and stimulating financial stability, but it also raises many questions and challenges for individuals and companies alike. In this article, we will discuss the details of this tax, starting with its concept and the products or services subject to it, going through how to prepare your facility to apply it and how to register for it, all the way to some of the penalties related to it. Are you ready to explore the world of VAT in Saudi Arabia? Let’s begin our journey to understand this important aspect of the Saudi tax system.
What is the value-added tax in Saudi Arabia?
Value Added Tax (VAT) is simply an indirect tax imposed in most countries around the world on all goods and services that are sold and purchased, with the exception of some of them, at every stage of supply and distribution, starting from production, through distribution, and ending with the stage of selling the good or service. For the final consumer. Value-added tax is a basic source of income that enhances countries’ budgets. Therefore, a value-added tax was imposed in Saudi Arabia in 2018 as part of the economic reform plan that aims to diversify sources of income and strengthen the government’s financial base. The Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority assumed responsibility for managing and implementing value-added tax in the Kingdom in cooperation with all concerned authorities.
Value-added tax represents an important source of revenue for the Saudi government and contributes to the provision of public services and the implementation of development projects in the country. This tax also enhances the transparency of the financial system and contributes to strengthening financial discipline in the private sector. The value-added tax in Saudi Arabia was passed in two stages. The first began in 2018 with the Kingdom’s commitment to implement a 5% value-added tax after the Gulf Cooperation Council countries agreed to adopt the tax in all GCC countries, and the Kingdom ratified this unified agreement in 2017. The second phase began in 2020 AD, when the decision to raise the value-added tax rate to 15% was implemented on all goods and services subject to it.
On which products is VAT charged?
The value-added tax in Saudi Arabia is imposed at a rate of 15% on all goods and services, with some exceptions, as shown in the following table:
| Category | Goods or services | comments |
| Food | all of them | – |
| Transport | Local transportation only | – |
| The property | Commercial real estate rental | – |
| education | Private education | The state bears the tax on behalf of citizens who benefit from private education services. |
| health care | Health care in private health centers | The state bears the tax on citizens who benefit from private health services. |
| Oil | The oil, petroleum derivatives, and local gas sectors | – |
| Metals | Supply of metals intended for investment (gold, silver, platinum) | Provided that the purity level of the metals is less than 99%. |
| Financial services | · Clear fees, commissions, or trade discounts.
· Insurance products, including health insurance |
|
| General and health insurance | · Personal accidents.
· work injuries. · Employer’s responsibility. · Responsibility towards others. · General liability. · Product liability. · Medical liability. · Professional responsibility. · Theft and burglary. · Dishonesty. · Insurance of funds in the Treasury and during transportation. · Other insurances that fall within the liability insurance points. · Vehicle insurance. · Property insurance. · Marine Insurance: Ship Hulls. · Marine insurance: transportation of goods. · Aviation insurance. · Energy insurance. · Engineering insurance. · Other branches of general insurance. · Mandatory health insurance. |
|
| Supplies or other cases | · Commission or any fee for brokerage or brokerage.
· Selling recalled goods as part of an insurance policy. · Sale of other business assets. · Consulting and administrative services. |
Requirements for applying value-added tax to establishments
You can verify the readiness of your company or facility with regard to all the details and requirements of applying value-added tax in Saudi Arabia as follows:
1-Large establishments
Here are some steps to check the readiness of your large facility:
- Determine the responsibilities of employees regarding tax applications.
- Accounting and classifying the facility’s commercial transactions according to tax application requirements.
- Preparing comprehensive accounting audit reports.
- Submitting tax reports regularly and creating an organization for them.
- Include supplier data, such as the tax registration number and tax certificate. And include a special tax clause in contracts with them.
- Include tax operations in the accounting data.
- Creating a technical infrastructure for tax application data.
2: Medium and small enterprises
Here are some steps to check the readiness of your medium or small facility:
- Understanding the tax system and determining tax policy for goods and services.
- Identify an employee to deal with the authority regarding the tax application.
- Organizing invoices and supplier data.
- Establishing an electronic system for invoices, prices, and sales.
- Submitting tax reports regularly and creating an organization for them.
How to register for VAT
Registration for value-added tax in Saudi Arabia is possible for establishments that conduct a commercial activity subject to value-added tax, or individuals whose annual revenues are more than 187,500 riyals and less than 375,000 riyals (registration is optional for individuals), or a group of two or more legal persons provided that they are residents of The Kingdom provides the legal conditions for this, so that when their application is approved, they are treated as one person for value-added tax purposes, without prejudice to the joint liability of each member of the group.
Here are the easy steps to register:
- Log in to the Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority’s website, Zatca.gov.sa, or use the Authority’s mobile application.
- Click on the “Electronic Services” menu.
- Choosing zakat, tax, and customs services.
- Choose tax services.
- Choose value-added tax.
- Choose the value-added tax registration service, either for establishments, individuals, or groups.
- Fill out the registration form.
- Wait until a notification of the tax certificate containing the tax number for the establishment or individual arrives when the request is completed.
Penalties in value-added tax
The Zakat and Tax Authority imposes penalties on those who violate value-added tax laws in Saudi Arabia. Here are the most notable ones:
- Failure to register in the value-added tax system within the statutory period: a fine of 10,000 riyals.
- Failure to submit a tax return within the statutory period: a fine of no less than 5% and no more than 25% of the value of the tax that should have been declared.
- Failure to pay the tax due within the statutory period: a fine equivalent to 5% of the value of the unpaid tax for each month or part thereof for which the tax was not paid.
- Failure to save tax invoices, books, records, and accounting documents within the statutory period: a fine not exceeding 50,000 riyals.
Qoyod: The best value-added tax service provider in Saudi Arabia
The Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority was keen to provide smart technical solutions that support medium and small enterprises in the process of implementing the value-added tax. Therefore, it has approved a number of tax service providers to assist your facility technically to be prepared to implement the tax by ensuring that the prices of goods or services are displayed inclusive of the tax, ensuring that sales receipts comply with tax requirements, and ensuring that the sales registration system complies with tax administration requirements.
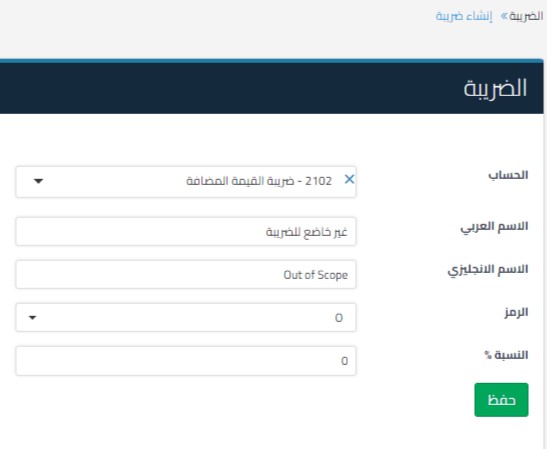
The Qoyod accounting system is the best provider of value-added tax services in Saudi Arabia. It provides you with the service of adding multiple taxes at specific rates so that you can use them later in your transactions. When creating a tax, you must fill out the following fields:
- Account: Current liability accounts.
- Name: in Arabic and English.
- Code: Includes 4 tax codes as specified by the Authority:
- Letter S stands for basic value added tax.
- The letter Z symbolizes zero tax.
- Letter E symbolizes tax exemption.
- The letter O stands for non-taxable. (It does not appear on the tax return because it is outside the scope of the tax.).
- The tax rate is to be applied.
When any tax you add is applied to your business transactions, Qoyod automatically calculates the tax accurately in the invoices it issues, and Qoyod prepares the tax return in accordance with the authority’s requirements to ensure full legal compliance for your facility.
Conclusion
We find that value-added tax in Saudi Arabia has an important role in supporting the local economy and generating revenues for the state, but it is also considered a challenge for individuals and companies in understanding its applications and adhering to them. By understanding its concepts and effects, individuals and businesses can better plan their financial strategies and ensure compliance with tax legislation.
Join the establishments that trust Qoyod to enhance transparency and integrity in tax applications in your establishment. Enjoy a free 14-day trial period without a credit card by subscribing to the Qoyod accounting system.

Join our inspiring community! Subscribe to our LinkedIn page and Twitter to be the first to know about the latest articles and updates. An opportunity for learning and development in the world of accounting and finance. Don’t miss out, join us today!




