This article provides a comprehensive overview of Corporate Governance principles, detailing the essential frameworks, structures, and specialized committees crucial for achieving transparency, accountability, and long-term sustainability. It outlines how effective governance, supported by digital accounting solutions like Qoyod Accounting Software, helps small and medium-sized businesses globally attract investment and reduce operational risks in a competitive environment. |
Corporate Governance is the organizational framework of laws, standards, policies, and procedures that regulate the relationships between management, shareholders, and other stakeholders such as employees, customers, suppliers, creditors, and the community. Its goal is to define authority, accountability, and decision-making mechanisms transparently and effectively. Globally, governance frameworks, often guided by bodies like the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), ensure the protection of rights and enhance integrity in the business environment.
This framework includes internal aspects, such as the board of directors’ structure and internal control, and external aspects, like governmental regulations and international standards. Originating from informal practices, Corporate Governance became a critical, mandatory framework following major corporate scandals, evolving into an essential tool for risk management and sustainability. For any small and medium-sized business aiming for scalable growth and international investment, mastering this structure is fundamental.
The Importance and Objectives of Corporate Governance
Corporate Governance aims to ensure accountability by clearly defining management’s responsibilities to the board and shareholders, which prevents overreach of authority and builds trust. It mitigates ethical and financial risks by imposing internal controls and regular disclosure. Studies indicate that companies with strong governance can reduce their losses by up to 20% during crises.
It fosters economic efficiency by improving strategic decision-making and the effective allocation of resources. Simultaneously, it guarantees transparency through financial reports and the disclosure of conflicts of interest, which protects the well-being of shareholders and stakeholders and attracts foreign investment. Cloud accounting systems and robust e-invoicing processes are now key digital enablers for meeting these transparency objectives, essential for tax compliance and accurate financial reporting.
The Golden and Core Principles of Corporate Governance
The “Five Golden Rules” of Corporate Governance are the fundamental principles that ensure the balance of power within a company, vital for any growing small and medium-sized business. These principles, derived from international standards like those from the OECD, form the basis of effective governance. Studies show that their application can enhance corporate value by 10-15%.
Detailed Breakdown of the Five Golden Rules

- Responsibility: The board of directors commits to guiding the company toward its strategic objectives, overseeing executive management, and ensuring compliance with laws, thereby safeguarding the interests of all parties.
- Accountability: Internal and external monitoring mechanisms (e.g., annual reports, general meetings) assess management performance, ensuring that no excessive authority is exerted.
- Awareness: This involves understanding the impact of company decisions on society and customers, promoting sustainability and social responsibility.
- Fairness: Guarantees equal treatment for all shareholders, large and small, and prevents discrimination or conflicts of interest.
- Transparency: Requires immediate and accurate disclosure of transactions and risks, adhering to established financial regulations.
Other Essential Principles
Additional principles enhance the comprehensive framework:
- Ethics: Defines the conduct of management and employees to prevent corruption.
- Risk Management: Utilizes predictive frameworks for financial and operational risks, a process greatly simplified by modern best accounting software.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Achieved through surveys and periodic dialogues.
- Shareholder Rights Protection: Includes the right to vote and access documentation.
- Fair Treatment: Ensures impartiality among all parties.
- Full Disclosure: Requires complete reporting of financial statements and relevant transactions.
Applying these principles reduces disputes and fosters trust, confirming their critical role in the global business context.
The Board of Directors Structure and Roles
The board of directors is the highest executive body in a company, responsible for strategic guidance and oversight of executive management. To ensure independence and mitigate conflicts of interest, global standards mandate a clear structure, often requiring a majority of Non-Executive Directors (NEDs).
Board Composition and Membership Criteria
- Majority of Non-Executive Directors: NEDs (those not involved in daily management) should form the majority to provide an objective view, enhancing oversight and reducing conflicts of interest.
- Independent Directors Ratio: A significant portion of the board must be Independent Directors, meaning they have no material relationship with the company or its executives, ensuring full autonomy.
- Membership Conditions: Criteria include relevant professional and academic competence, leadership and strategic planning capability, financial acumen, and the absence of conflicts of interest or prior convictions/bankruptcy.
Board Responsibilities
- Strategy Formulation: Defining the long-term vision, objectives, and main policies, along with approving budgets and annual plans.
- Oversight of Executive Management: Appointing and monitoring the CEO and senior executives, with a clear separation between the roles of the Board Chair (leading the board) and the CEO (managing daily operations) to prevent concentration of power.
- Risk Management: Establishing a comprehensive framework to identify and monitor financial, operational, and legal risks, often through specialized committees.
Member Responsibilities and Procedures
- Chair’s Responsibilities: Managing board meetings (typically no less than four annually), ensuring adequate information is provided to members, and promoting communication with shareholders.
- Independent Members: Provide neutral opinions, often chairing the Audit and Remuneration committees, and maintaining information confidentiality.
- Periodic Meetings and Performance Evaluation: Holding meetings at least every three months, recording minutes, and conducting an annual evaluation of the board and individual members using objective criteria, with ongoing training for members.
This structured board governance builds market confidence and supports strategic objectives for all businesses.
Shareholders’ Rights and General Assembly Meetings
Shareholders’ rights are a cornerstone of Corporate Governance, ensuring fair treatment for all shareholders regardless of size, with oversight mechanisms that protect their interests through effective disclosure and participation in core decisions. These rights include supervising management, ensuring fair profit distribution, and the ability to challenge unjust decisions.
General Shareholders’ Rights

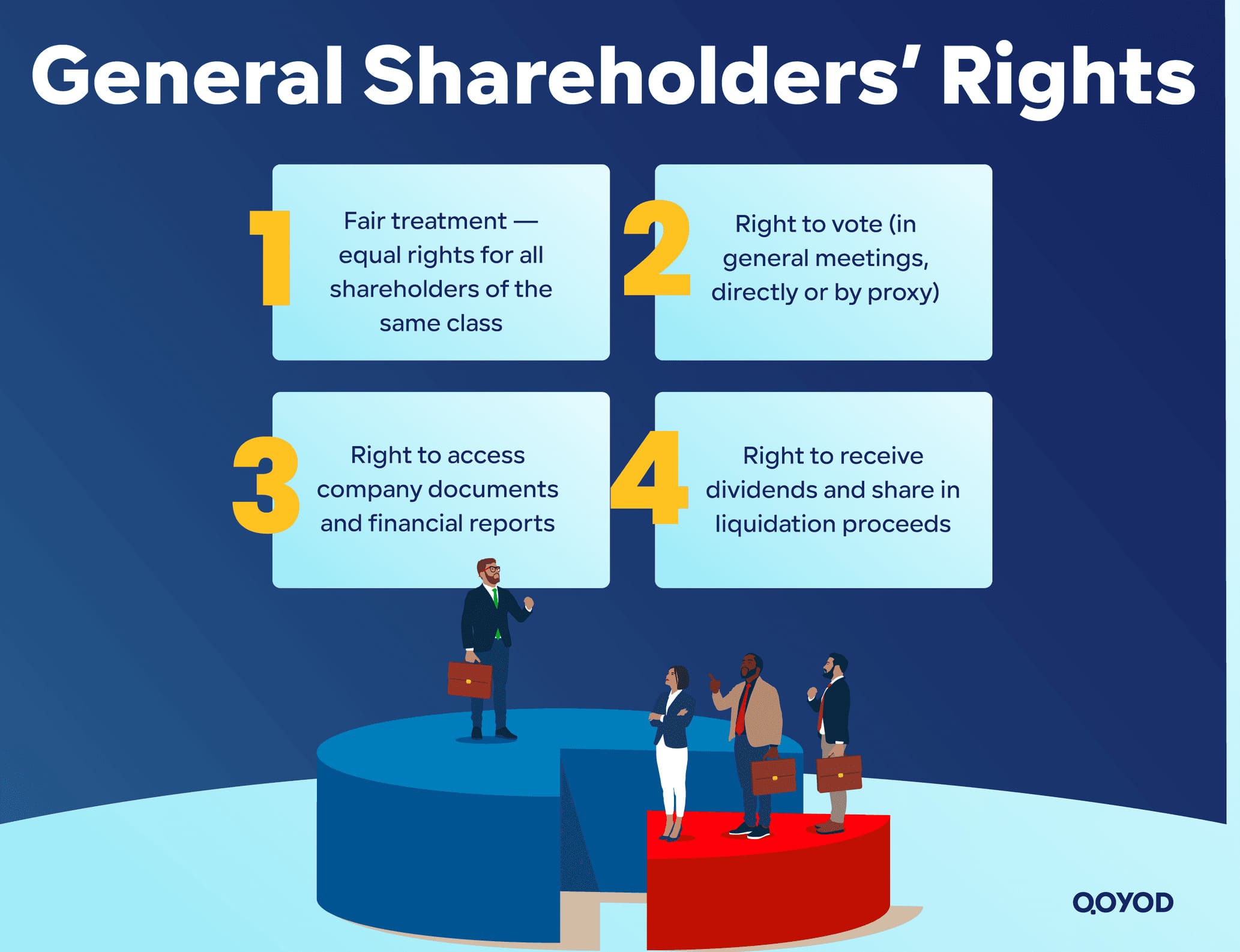
- Fair Treatment: Prohibiting discrimination among shareholders of the same class of shares and guaranteeing that no right is withheld.
- Voting Right: Every shareholder has the right to vote in Ordinary or Extraordinary General Assembly Meetings, either personally or through a proxy.
- Disclosure and Access to Documents: The right to access the founding contract, bylaws, financial statements, and board reports without delay, along with knowledge of material non-public developments.
- Dividend Distribution and Liquidation: Receiving a fair share of cash or stock dividends, and a share of assets upon company liquidation after settling debts.
General Assembly: Competencies and Procedures
- Ordinary General Assembly (AGO): Held annually within six months of the financial year-end. Competent to approve financial statements, distribute dividends, appoint auditors, and elect board members.
- Extraordinary General Assembly (EGM): Held when needed to amend bylaws, increase/decrease capital, merge, liquidate, or approve major transactions.
- Agenda and Meeting Management: Prepared by the board with advance notice (often 21 days globally). Shareholders may discuss items and direct questions to management or auditors, with recorded minutes and the ability to legally challenge decisions.
- Remote Participation: Modern governance increasingly allows the use of technology (video conferencing) for attendance and voting, ensuring voting secrecy and accessibility for the maximum number of shareholders.
These strong shareholder rights boost market transparency and participation, critical factors for attracting global investors.
Specialized Committees
The Corporate Governance system comprises a set of specialized committees that support the board of directors in oversight and decision-making professionally and independently. These committees are the most important tools for the practical application of good governance.
| Committee | Key Responsibility | Core Function | Composition Requirement |
| Audit Committee | Financial oversight and internal control | Reviews financial statements, ensures quality of financial reporting, recommends and evaluates external auditors. | All members must be non-executive, majority independent. |
| Remuneration Committee | Compensation policy and structure | Sets policies for director and executive compensation, linking incentives to long-term performance. | Independent oversight ensures fairness and transparency. |
| Nominations Committee | Board and committee member selection | Sets criteria for nomination, assesses competency, ensures independence, and screens candidates for the general assembly. | Focuses on skills gap analysis and independence. |
| Risk Management Committee | Oversight of risk framework and compliance | Identifies and classifies risks (financial, operational, reputational), monitors mitigation plans, and reviews governance policies. | Essential for sustainable operation and compliance. |
The Role of Key Committees

- Audit Committee: Ensures the integrity of internal controls and financial reporting, a process streamlined by leveraging reliable Cloud accounting system reports.
- Remuneration Committee: Works to establish clear criteria for fixed and variable compensation, ensuring fairness and competitiveness while aligning incentives with shareholder interests.
- Nominations Committee: Focuses on the quality of board composition, preparing a “job description” for board seats and ensuring a sufficient number of independent members.
- Risk Management Committee: Updates governance policies and monitors compliance, reporting the level of key risks and recommendations for improvement to the board.
Through this integrated structure of specialized committees, the board of directors transforms from a merely formal supervisory body into an effective regulatory system where responsibilities are clearly distributed, powers are separated, and the quality of decisions and transparency within the company are enhanced.
Read Also: Account Audit Guide: Steps, Importance, and Process in Saudi Arabia
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Corporate Governance
What is Corporate Governance?
The regulatory framework (laws, standards, procedures) that organizes relationships between management, shareholders, and stakeholders to define authorities and decision-making mechanisms with transparency and effectiveness.
Why is Corporate Governance Important?
It enhances accountability, reduces ethical and financial risks, improves economic efficiency, ensures transparency, and attracts investments, potentially reducing losses by up to 20% during crises.
What are the Five Golden Principles?
Responsibility, Accountability, Awareness, Fairness, and Transparency. They form the core ethical and procedural foundation derived from international standards (e.g., OECD).
How is the Board of Directors typically structured?
It consists of an odd number of members, with a majority of Non-Executive Directors and a minimum proportion of Independent Directors, all elected by the General Assembly.
What are the Board's responsibilities?
Setting strategy, overseeing executive management, managing risk, and maintaining a clear separation between the Chair and CEO roles.
What are the main Shareholders' Rights?
Fair treatment, the right to vote in Assemblies, full disclosure, fair distribution of profits, and access to documents like financial statements.
Ordinary vs. Extraordinary General Assembly?
Ordinary (Annual): Approves financials, dividends, elects the board. Extraordinary (As needed): Amends bylaws, changes capital, or approves mergers/liquidation.
What is the role of specialized committees?
Audit Committee: Financial oversight; Remuneration: Compensation structure; Nominations: Candidate selection; Risk Management: Risk identification and monitoring.
How does digital accounting support Governance?
Tools like Qoyod automate accurate financial statements, risk reports, and ensure compliance with e-invoicing and tax compliance standards, facilitating timely disclosure.
What is the outcome of good Governance?
It leads to sustainable growth, reduces legal disputes, enhances market confidence, and increases corporate value by attracting major investments.
Conclusion: Corporate Governance – The Foundation for Sustainable Success
Corporate Governance is the strategic framework that ensures the balance between the interests of shareholders and stakeholders, utilizing principles of transparency, accountability, an effective board structure, specialized committees, and robust shareholder rights. This framework reduces risks and enhances economic efficiency in a competitive business environment.
To practically achieve this governance, particularly within small and medium-sized businesses globally, adopting advanced digital tools is essential. Try Qoyod Accounting Software now to make your business operations easier and more accurate with solutions designed for modern businesses. Qoyod, as a cloud-based best accounting software, supports full compliance with governance standards through accurate financial statements management, automated reporting, risk tracking, and transparent disclosure. Its features, including integration with digital invoicing systems and profit tracking, ease the work of boards and committees, ensuring fair profit distribution and regulatory compliance.
By implementing these principles and leveraging digital tools, companies transform challenges into opportunities for growth, maintaining trust and sustainability in a rapidly changing global market.