Excerpt:
An in-depth look at the challenges small and medium-sized businesses face when measuring Net Sales and the best accounting solutions for accurate financial reporting.
Net Sales is a critical financial metric that reflects the actual revenue generated by a company over a specific period, after deducting returns, allowances, and discounts from Gross Sales. While Gross Sales represents the total value of all sales made, providing an often-inflated impression of financial performance, Net Sales offers a much clearer and more accurate picture of a company’s true revenue.
Gross Sales is calculated by multiplying the number of units sold by the unit price, and it includes all sales, regardless of whether they are returned later. Net Sales, conversely, accounts for factors that reduce the final value of sales, such as:
- Sales Returns: Goods returned due to defects or customer dissatisfaction.
- Sales Allowances: Reductions granted due to issues like product damage or variance from advertised specifications.
- Sales Discounts: Incentives offered to encourage purchases, such as cash discounts for early payment.
This makes Net Sales a more realistic and accurate measure for assessing actual financial performance compared to Gross Sales.
Business owners and financial analysts rely on Net Sales to understand the amount of revenue truly retained, aiding in strategic decisions about pricing, marketing, and inventory management. Furthermore, the company’s expenses and revenues compiled in financial reports heavily depend on Net Sales figures, making it the starting point for profitability analysis and overall performance evaluation.
Key Components Affecting Net Sales Calculation
Several core elements directly contribute to determining the final sales value recorded in the financial statements:
-
Sales Returns
These are sales that customers return to the company, often due to product defects or dissatisfaction. When returns occur, their value is deducted from Gross Sales to determine the actual revenue realized, thereby reducing Net Sales and reflecting the true state of earnings.
-
Sales Allowances
These are price reductions granted to customers after a sale due to issues like product damage or discrepancies between the advertised and actual product. Allowances are also treated as a deduction from Gross Sales because they reduce the value the company retains post-sale.
-
Sales Discounts
These are deducted from Gross Sales and include various types, such as cash discounts to encourage early customer payment or promotional discounts to incentivize sales volume. These discounts are direct costs that affect revenue and are therefore subtracted from the gross total to accurately assess Net Sales.
Taking these factors into account ensures that the gross sales figures are corrected to reflect the actual value of revenue received by the company after handling all necessary adjustments. This makes Net Sales a more accurate and reliable indicator of sales performance compared to Gross Sales, supporting sound financial and marketing management decisions based on carefully calculated data.
Key Takeaway: Sales returns, allowances, and discounts are central factors that directly influence the Net Sales calculation, and are deducted from gross revenue to arrive at a net figure that reflects the company’s true performance.
Net Sales Calculation Formula with Practical Examples
The formula for calculating Net Sales relies on subtracting certain elements from Gross Sales to reflect the actual value of sales retained by the company.
The Basic Formula
Net Sales = Gross Sales – Sales Returns – Sales Allowances – Sales Discounts
- Gross Sales: The total value of all sales achieved over a period, including cash and credit sales, without any deductions or adjustments.
- Sales Returns: The value of goods returned by customers, which are deducted because the company did not retain this revenue.
- Sales Allowances: Post-sale reductions offered to customers due to product or service issues, such as damage or non-conformance with specifications.
- Sales Discounts: Reductions given to customers to encourage purchases, such as early payment or bulk discounts.
Practical Calculation Examples
- Example 1: A company records Gross Sales of $100,000 during a fiscal year. During the same period, $5,000 worth of goods were returned, $2,000 in allowances were granted, and $3,000 in discounts were applied.
Net Sales = $100,000 − $5,000 − $2,000 − $3,000 = $90,000
The Net Sales for the company is $90,000.
- Example 2: Another company reports Gross Sales of $250,000, with returns amounting to $10,000, allowances of $3,000, and discounts of $7,000.
Net Sales = $250,000 − $10,000 − $3,000 − $7,000 = $230,000
The Net Sales for this company is $230,000.
This calculation method enables companies to determine the actual remaining revenue after accounting for all adjustments to Gross Sales, allowing for a more accurate assessment of financial performance and supporting sound, data-driven decision-making.
The Importance of Net Sales in Financial Analysis
Net Sales is a fundamental indicator in financial analysis that cannot be overlooked, as it reflects the true value of revenue after all necessary adjustments. Its importance lies in providing an accurate view of the actual income available to the company, thus helping to assess operational efficiency and profitability more realistically than Gross Sales.
By monitoring Net Sales, businesses can measure the impact of discounts and returns on their sales outcomes and, consequently, on their business profitability. Significant gaps between gross and Net Sales may indicate underlying issues with pricing strategies or product quality, necessitating continuous review and improvement.
- Profitability Analysis: Net Sales is the essential input for calculating various profit margins, serving as a vital indicator of the returns the business is genuinely generating.
- Financial Reporting: Net Sales plays a direct role in preparing financial statements, such as the Income Statement, helping to paint a clear picture of the financial situation and acting as a foundation for strategic decisions regarding investment, expansion, pricing, and resource management.
Companies that regularly track their Net Sales are better equipped for sound financial planning and cash flow forecasting, which enhances their financial stability in the long run.
Summary: Net Sales is a precise financial measure reflecting actual revenue after deductions and is a foundational metric in financial analysis and evaluating a company’s financial performance.
Relationship Between Net Sales and Other Income Statement Items
This table illustrates how Net Sales connects with all essential items on the Income Statement, highlighting its pivotal role in financial performance evaluation.
| Income Statement Item | Relationship with Net Sales |
| Net Sales | Represents revenue after deducting returns, allowances, and discounts from Gross Sales. |
| Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) | Deducted from Net Sales to calculate Gross Profit. |
| Gross Profit | The difference between Net Sales and COGS, reflecting product profitability before operating expenses. |
| Operating Expenses | Deducted from Gross Profit to arrive at Operating Income. |
| Operating Income | Reflects the company’s profit before non-operating income or expenses. |
| Other Revenues and Expenses | Added to or subtracted from Operating Income to reach Net Income Before Taxes. |
| Net Income After Taxes | The final profit reported on the Income Statement, fundamentally dependent on Net Sales levels and the impact of all preceding items. |
| Impact of Net Sales | An increase in Net Sales means higher Gross Profit and greater profitability potential; every subsequent item directly depends on it. |
| Performance Monitoring | Net Sales is the starting point for analyzing profitability, operational efficiency, and the sustainability of financial performance. |
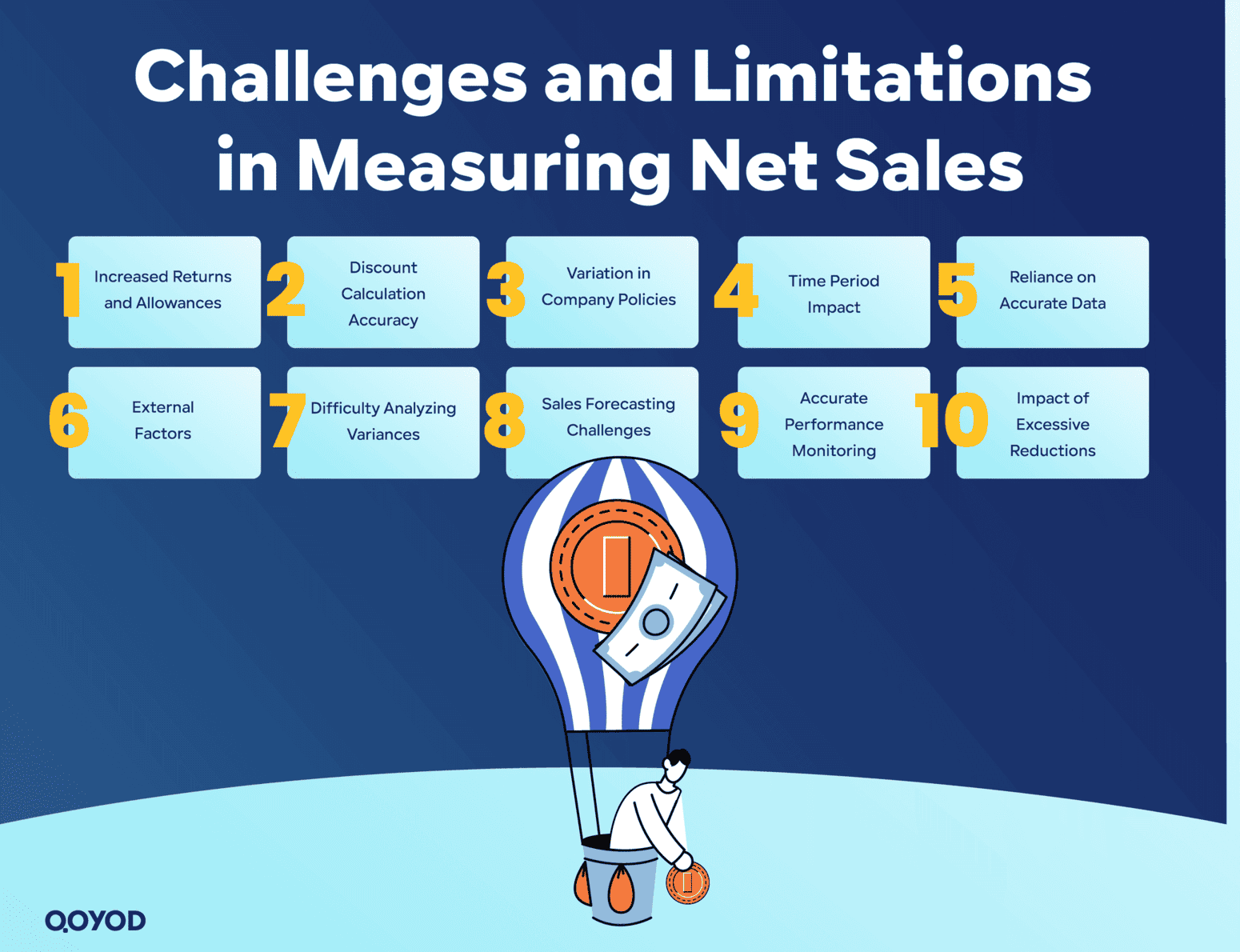
Challenges and Limitations in Measuring Net Sales
Accurately measuring Net Sales can present several challenges for small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs):
-
Increased Returns and Allowances
Frequent returns and excessive allowances diminish Net Sales, potentially signaling problems with product quality or customer satisfaction, making accurate revenue estimation difficult.
-
Discount Calculation Accuracy
Errors in recording and calculating discounts (promotional or early payment) can skew Net Sales data, affecting the integrity of financial reports.
-
Variation in Company Policies
Differences in accounting policies for applying discounts and allowances across companies make accurate comparison of Net Sales figures difficult across sectors or competitors.
-
Time Period Impact
Recording sales or returns in different accounting periods can lead to inconsistency and fluctuation in figures, complicating period-specific financial performance analysis.
-
Reliance on Accurate Data
A lack of updated data or inconsistent recording leads to difficulties in calculating Net Sales accurately and reliably.
-
External Factors
Seasonal changes, market fluctuations, or competition can cause unexpected shifts in Net Sales, making forecasting and analysis challenging.
-
Difficulty Analyzing Variances
The complexity of contributing elements like returns and discounts makes it hard to pinpoint the exact reasons for the difference between gross and Net Sales.
-
Sales Forecasting Challenges
Budget estimates and financial targets rely heavily on Net Sales. Any error in this calculation impacts the quality of financial planning.
- Accurate Performance Monitoring
Without reliable Net Sales data, it becomes difficult to accurately track sales team performance and take corrective actions when necessary.
-
Impact of Excessive Reductions
Offering significant discounts may boost sales volume but reduces Net Income, potentially negatively affecting the company’s actual profitability.
Overcoming these challenges necessitates developing accurate accounting systems, improving data quality, and adopting advanced analytical tools to ensure the reliability and validity of Net Sales data, thereby supporting sound financial decision-making.
` The Accounting Difference Between Net Sales and Gross Sales
Gross Sales reflects the total value of a company’s sales before any adjustments. Net Sales, however, represents the actual amount remaining after deducting returns, allowances, and discounts, making it a reflection of the precise revenue realized.
| Feature | Gross Sales | Net Sales |
| Definition | Total revenue from all sales transactions. | Gross Sales minus returns, allowances, and discounts. |
| Accuracy | Generally overstated; does not account for revenue reductions. | Reflects the true financial reality and actual retained revenue. |
| Reporting Use | Provides a general overview of sales volume. | The foundation for calculating Gross Profit and subsequent Income Statement items. |
| Comparability | Less useful for objective comparison across companies due to unadjusted figures. | Provides an objective benchmark for comparison after standardized adjustments. |
| Tax Impact | Less accurate for tax reporting as it includes non-retained revenue. | Essential for tax compliance and transparency as it reflects actual taxable revenue. |
Impact on Accuracy and Financial Analysis:
While Gross Sales offers a glimpse into sales volume, it often overestimates because it disregards revenue-reducing factors. Net Sales accurately reflects the financial reality, enabling correct profitability analysis.
Impact on Reporting:
Reliance solely on Gross Sales in reports can mislead investors and decision-makers due to an inflated perception of profitability. Reports based on Net Sales present a transparent and genuine picture of the company’s financial performance.
Importance in Income Statement Preparation:
Net Sales is the starting point for calculating Gross Profit and significantly impacts all subsequent financial figures on the Income Statement. Ignoring it leads to inaccurate results in calculating profits and losses.
In summary, Net Sales provides a true financial picture supporting sound financial decisions, while Gross Sales offers a general but potentially inflated view. The distinction between the two severely impacts the accuracy of financial reports and performance analysis. Cloud accounting software is essential for businesses to maintain this distinction accurately.
FAQ: Common Questions About Net Sales
What is Net Sales?
Net Sales is the value of Gross Sales after deducting returns, allowances, and discounts. It reflects the true revenue realized after adjusting initial figures.
How is Net Sales calculated?
It is calculated using the formula: Net Sales = Gross Sales – Returns – Allowances – Discounts.
What is the difference between Net Sales and Gross Sales?
Gross Sales does not include discounts or returns, whereas Net Sales accounts for them, reflecting the true retained revenue.
Why is Net Sales important in financial analysis?
Because it reflects the company's actual financial performance, it helps in making informed pricing and marketing decisions and accurately analyzing profitability.
How do returns affect Net Sales?
Returns reduce Net Sales because they represent products returned that did not generate revenue for the company.
In Conclusion
Net Sales is the cornerstone for understanding the true financial performance of any organization. It is not just a statistical figure but a reflection of the actual revenue a company achieves after accounting for factors like returns, discounts, and allowances. The precise distinction between Net Sales and Gross Sales allows businesses to make financial and strategic decisions based on accurate and transparent data.
With the increasing importance of accuracy and transparency in finance, Qoyod Accounting Software provides a sophisticated and efficient tool for managing and recording Net Sales with high precision. The system enables the accurate preparation of final accounting entries and ensures that all accounting operations related to sales and adjustments are tracked in an organized manner.
By leveraging Qoyod’s features, accountants and financial departments can keep Net Sales data updated, facilitating the preparation of reliable and accurate financial reports. This contributes to better evaluation of the company’s financial performance and the achievement of growth objectives and optimal resource management. Integrating Qoyod into financial operations is a vital strategic step toward achieving sustainable financial transparency and efficiency.
Try Qoyod Accounting Software now to make your business operations easier and more accurate with solutions designed for modern businesses.