| Expert Summary:
This article outlines essential accounting policies and best practices for their application. Discover how Qoyod Accounting Software can integrate seamlessly to enhance financial and administrative performance for your business. |
Accounting policies are the core of the financial and administrative processes for every organization seeking transparency and accuracy in its financial reports. They serve as the practical framework that finance departments must adhere to when processing, recording, and presenting all economic events and transactions experienced by the company.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) globally are increasingly focused on establishing clear and uniform accounting policies and following professional best practices. These policies ensure alignment with the requirements of regulatory bodies and international standards such as IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards).
These policies set controlling rules and procedures, from the mechanism for revenue recognition to choosing a depreciation method, estimating end-of-service expenses, and valuing inventory items. This uniformity allows for the standardization of measurement and disclosure methods, reducing conflicting personal judgments among accountants or different departments.
The adoption of clear accounting policies is paramount. They facilitate the comparison of performance across financial periods and between peers in the same sector. Furthermore, they enable regulators, auditors, and investors to review data with greater confidence due to the consistency in reporting methods. Accounting policies ensure accurate recording of transactions and uphold the prudence principle in assessing future events and potential liabilities, preventing company results from being skewed by hasty estimates or unprofessional handling of sensitive items.
Accounting policies always originate from accepted accounting principles but take on a practical application. While principles represent the general theoretical framework governing accounting work (like the Accrual Basis or Consistency Principle), policies are the specific tools and methods adopted by each company, according to its business nature, to produce accurate, standardized, and appropriate financial reports for internal and external use.
Thus, adopting accounting policies that align with a company’s nature and objectives is a pivotal step toward financial governance and sustainable success. It enhances the credibility of financial statements, supports management and investment decision-making, and establishes a transparent and healthy financial environment that meets the expectations of the market and regulatory bodies.
The Difference Between Accounting Policies and Accounting Principles
A fundamental distinction exists between accounting policies and accounting principles:
- Accounting Principles are a set of basic rules and guidelines, adopted internationally or locally, that define how financial transactions should be recorded and presented, such as the Accrual Basis, Historical Cost Principle, Revenue Recognition Principle, and others.
- Accounting Policies are the practical translation of these principles. They typically embody the entity’s choices of specific accounting methods that ensure compliance with the principles. Examples include selecting a depreciation calculation method (Straight-Line or Declining Balance) or adopting an inventory valuation method (FIFO or LIFO).
In summary, principles provide the general, uniform framework, while policies are the actual application chosen by management to suit the company’s specific activity, structure, and organizational .
Importance of Accounting Policies in Ensuring Financial Accuracy and Transparency
Accounting policies play a critical role in achieving accuracy and transparency in any entity’s financial reports. They act as the reference point organizing how financial transactions are recorded and economic events are measured, which directly impacts the reliability of financial results and statement information.
The presence of clear, uniform accounting policies within a company ensures consistency in recording and reporting methods across different departments and branches. This reduces personal estimates and resulting deviations, making it easier to detect and track potential errors or manipulation, and strengthening adherence to local and international accounting standards.
Key Positive Effects of Adopting Robust Accounting Policies
- Increased Transparency: Reduces errors and financial risks by establishing documented, precise procedures for all steps of financial work.
- Enhanced Investor and Stakeholder Trust: Facilitates the reading and comparison of financial statements across years and similar companies.
- Streamlined Regulatory Compliance: Provides a clear framework that improves the quality of financial disclosure, compelling the accounting team to process transactions according to pre-defined controls.
- Informed Strategic Decisions: By creating a credible and stable environment for presenting financial results, policies improve the accuracy of financial analyses and the reliability of management’s future forecasts.
In short, accounting policies form the foundation upon which the financial systems of a modern company are built. They are the true guarantee of reports’ reliability and transparency, ensuring management can make sound strategic decisions that enhance the company’s ability to compete and grow in a transparent and disciplined business environment.
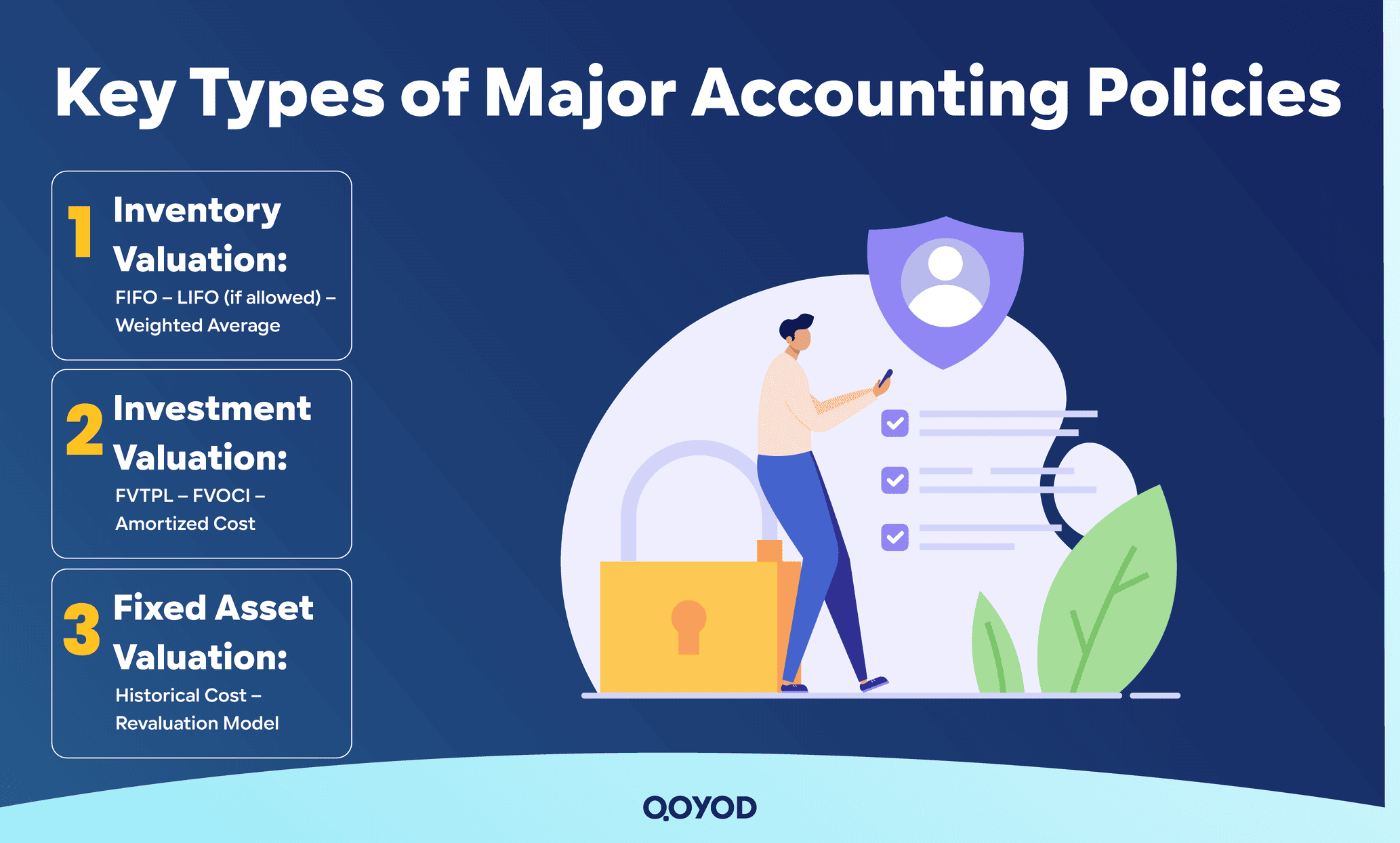
Key Types of Major Accounting Policies
Diverse accounting policies are fundamental to organizing financial statements and explaining business results. They reflect the technical choices management adopts for handling financial items and situations, ensuring consistency in classification, measurement, and disclosure.
The choice of accounting policies depends on the entity’s nature of business, adopted accounting standards, and regulatory/comparability requirements across financial periods.
-
Inventory Valuation Policies
Companies adopt various policies for inventory valuation, such as First-In, First-Out (FIFO), Last-In, First-Out (LIFO – where permitted), or Weighted-Average Method. These policies directly impact the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) and profits. In an inflationary environment, the choice of policy affects the profit margin and taxes.
-
Investment Valuation Policies
How investments are classified in financial statements is determined by policies such as Fair Value Through Profit or Loss (FVTPL), Fair Value Through Other Comprehensive Income (FVOCI), or Amortized Cost. These policies directly reflect market fluctuations in profits or other income items, influencing the reading of a company’s results and earnings sustainability.
-
Fixed Asset Valuation Policies
Common policies for valuing fixed assets include Historical Cost or Revaluation. Each policy defines how the value of assets appears on the balance sheet and whether changes in market value will be recognized in the future, thus impacting the company’s financial strength and its attractiveness to investors and financial observers.
-
Depreciation and Amortization Policies
Accounting policies for depreciation rely on selecting the Straight-Line, Declining Balance, or Units of Production method. These choices affect how the asset’s cost is distributed over its useful life, which in turn impacts annual profits and the residual value of assets in the statements.
-
Research and Development (R&D) Cost Treatment Policies
Companies define whether R&D costs are treated as direct expenses or capitalized as assets with future benefits. This affects the profitability efficiency of different financial periods and the accuracy of assessing the entity’s future performance.
-
Foreign Currency Translation Policies
Accounting policies address exchange rate differences resulting from transactions in foreign currencies, either through immediate treatment or deferral of recognition in the income statement. These policies influence the stability of financial results, especially for companies dealing internationally, requiring high transparency in handling international assets and liabilities.
Each of these policies is a strategic methodological choice with a profound impact on a company’s financial results. Therefore, entities and regulatory bodies are keen to disclose them in the financial notes to ensure comparability, transparency, and fair evaluation.
The Link Between Accounting Policies and IFRS
International and local accounting standards play a pivotal role in shaping the accounting policies adopted by modern organizations. These standards serve as the main reference to ensure the consistency and reliability of financial reports, which enhances stakeholder confidence and achieves regulatory compliance in the evolving market.
Accounting Policies and IFRS Standards
Accounting policies are based on applying the instructions issued by the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), set by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). These standards ensure that financial statements are prepared clearly, transparently, and comparably between companies globally, imposing a unified framework for policy implementation. IFRS standards enhance the quality of financial disclosure and set clear policies for revenue recording, asset valuation, liability treatment, and profit fluctuation recognition. Companies are required to continually update their policies to keep pace with improvements in IFRS.
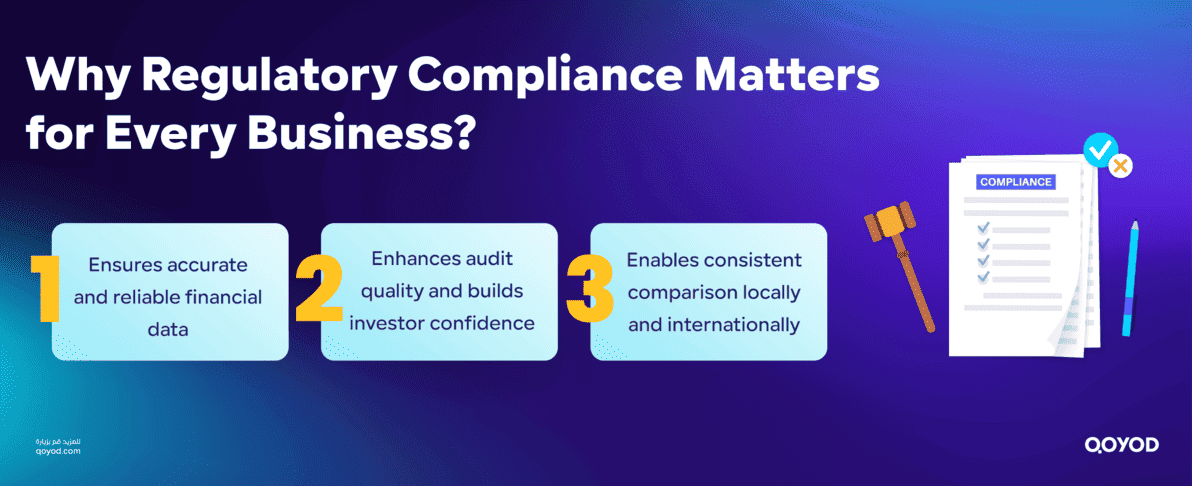
The Importance of Regulatory Compliance
While IFRS sets the global benchmark, local regulatory bodies adapt these standards to suit the local market, considering specific tax rules and local environmental requirements. Compliance with these local standards ensures:
- Accurate and Reliable Financial Data: Meeting the requirements of regulatory bodies and external auditors.
- Enhanced Audit Quality: Improving internal and external auditing processes and boosting investor confidence through transparent financial disclosure.
- Facilitating Financial Comparison: Making local and international performance comparisons easier, which supports investment decisions and promotes a healthy business environment.
Learn More: Account Audit Guide: Steps, Importance, and Process in Saudi Arabia
In conclusion, adherence to both global standards like IFRS and relevant local mandates is the cornerstone for formulating approved accounting policies. This ensures that financial statements are prepared and presented systematically and professionally, contributing to sustainable institutional growth.
Practical Examples and Comparisons in Accounting Policies
Accounting policies are the backbone of transaction recording and financial reporting, varying significantly between companies based on their activity, size, and strategic objectives. The following comparative details highlight the impact of these policies:
Aggressive vs. Conservative Policies and Their Impact
| Feature | Aggressive Policies | Conservative Policies |
| Revenue Recognition | Tends to recognize revenue earlier and reduce provisions. | Focuses on over-estimating costs and risks. |
| Result | Shows high, temporary profitability, but exposes the company to greater risks (e.g., inaccurate risk disclosure). | Reduces declared profits but enhances transparency and minimizes future financial surprises. |
| Examples | Using less rigorous depreciation methods or reducing the provision for doubtful debts. | Increasing debt provision or immediately expensing R&D costs. |
The impact of these two approaches is evident in how the financial position is presented and how performance is evaluated by investors and financial analysts.
Comparing Company Policies by Size and Industry
| Company Type | Common Accounting Policies | Policy Impact |
| Large Enterprises | Strong adherence to IFRS, advanced policies for asset valuation and hedging, high disclosure transparency. | Boosts confidence in international markets, strong support for financing and investment. |
| Small and Medium Businesses (SMEs) | Adopts simpler, sometimes simplified, policies based on regulatory needs; more conservative in financial diagnosis. | High flexibility and speed of adaptation, but challenges in attracting external funding. |
| Heavy Industry Companies | Accelerated depreciation policies, precise valuation of inventory and fixed assets due to asset nature and intensive maintenance needs. | Regulatory satisfaction and higher accuracy in production costs. |
| Tech and Services Companies | Valuation policies for intangible financial investments, enhanced disclosure of digital assets and software. | Reflects continuous innovation and updating, strong impact on market value. |
These examples and comparisons illustrate how accounting policies interact with market conditions, business nature, and entity size. Understanding and applying the right policies can significantly impact financial reports and the company’s success in achieving its strategic goals.
FAQ: Top 10 Common Questions About Accounting Policies
What are Accounting Policies?
Accounting policies are the rules and procedures adopted by an entity to organize and document financial transactions and prepare financial reports in compliance with local and international standards.
What is the difference between policies and principles?
Accounting principles are the general, global rules, while accounting policies are the practical applications decided by each company to implement these principles according to its specific circumstances.
Why do companies adhere to specific policies?
To ensure consistency and transparency in financial reports, which enhances trust among investors and stakeholders and aids in making informed decisions.
How do accounting policies affect a company's results?
The selection of policies, such as inventory valuation or depreciation methods, affects net profit and the book value of assets, consequently impacting the company's financial image.
What is the role of IFRS standards in policy formulation?
IFRS standards set the general frameworks upon which accounting policies are built to achieve globally unified and transparent financial reports.
Do policies differ between companies based on size?
Yes, large companies adopt complex, advanced methods, while SMEs often follow simpler policies appropriate to their activity.
What is the difference between aggressive and conservative policies?
Aggressive policies yield more optimistic financial reports, while conservative ones exercise caution and reduce fluctuations in financial results.
How do policies support strategic decision-making?
They provide accurate and reliable data that helps management evaluate financial performance and plan investments and financing.
Why is disclosure of policies important in financial statements?
Disclosure enhances transparency and allows stakeholders to understand the basis for preparing financial reports and any changes that might affect the results.
How does Qoyod Accounting Software contribute to implementing policies?
Qoyod allows for the accurate implementation of accounting policies through an integrated system that supports the preparation of financial reports compliant with international and local standards, facilitating documentation and review.
AT SUM UP:
Accounting policies are the foundation upon which the quality and transparency of financial reports in any enterprise are built. They contribute to standardizing recording, measurement, and disclosure procedures, which supports the accuracy of financial information and enhances the confidence of investors and stakeholders. Their importance is highlighted by their direct impact on financial results, corporate governance, and the ability of regulatory bodies to monitor financial performance efficiently.
Key takeaways discussed in this article include: the definition of accounting policies and their distinction from principles, their role in ensuring financial report accuracy and strategic decision-making, the main types of policies (e.g., inventory, investment, fixed assets), and their relationship with IFRS.
To achieve effective implementation of accounting policies, the following practical steps are recommended:
- Continuously update policies in line with developments in international and local standards.
- Provide adequate training for accounting staff on the accurate application of these policies.
- Clearly document policies and make them accessible to all relevant parties.
- Conduct periodic reviews to ensure policy effectiveness and adjust them as needed.
In this context, Qoyod Accounting Software emerges as an integrated software solution that helps enterprises apply accounting policies effectively. It provides a comprehensive accounting system that supports the preparation of financial reports in accordance with international and local standards, complete with features for documentation, review, and continuous updating. Qoyod also facilitates financial analysis and provides accurate insights for decision-makers, boosting companies’ ability to manage their financial resources efficiently and achieve their strategic goals.
Try Qoyod Accounting Software now to make your business operations easier and more accurate with solutions designed for modern businesses.