| Excerpt ZATCA e-invoicing Phase 2 is compulsory for eligible Saudi SMBs, requiring integration of compliant accounting systems, like Qoyod, with the FATOORAH portal for real-time invoice clearance and validation. This shift is critical for ensuring full regulatory adherence, reducing audit risk, and enhancing financial transparency within the Kingdom’s digital economy |
Introduction
In this comprehensive article provided by the Qoyod Accounting Software blog, we cover the fundamentals of the account audit process and its increasing importance for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) in Saudi Arabia’s rapidly evolving business environment. The role of the account audit is now a cornerstone for ensuring that financial data accurately presents a fair and clear picture of a company’s financial performance and position.
For every business, from new startups in Riyadh to established Jeddah firms, compliance with accounting standards and conducting internal and external auditing is a corporate necessity. This is crucial for fostering trust among investors, stakeholders, and regulatory bodies like the Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority (ZATCA). With the Kingdom’s focus on economic diversification and financial governance, driven by Saudi Vision 2030, a robust account audit framework is integral to achieving sustainable growth. This guide offers a practical, integrated reference for every company seeking excellence and full compliance in the Saudi market.
The Account Audit Process and Its Importance for KSA Businesses
An account audit, often referred to as a financial review, is an independent and objective process of examining a company’s financial information, such as financial statements, internal control structures, and related data. The primary objective is to issue a professional opinion on whether this data is presented fairly and truthfully, in accordance with adopted accounting standards.
An audit is vital for ensuring the quality and reliability of financial information. It offers assurance to external users (investors, creditors, regulators) that the company has adhered to fundamental accounting principles and has not omitted material disclosures. For companies in Saudi Arabia, a comprehensive account audit covers all material financial aspects, examining not only the numbers but also the procedures and controls that generate them.
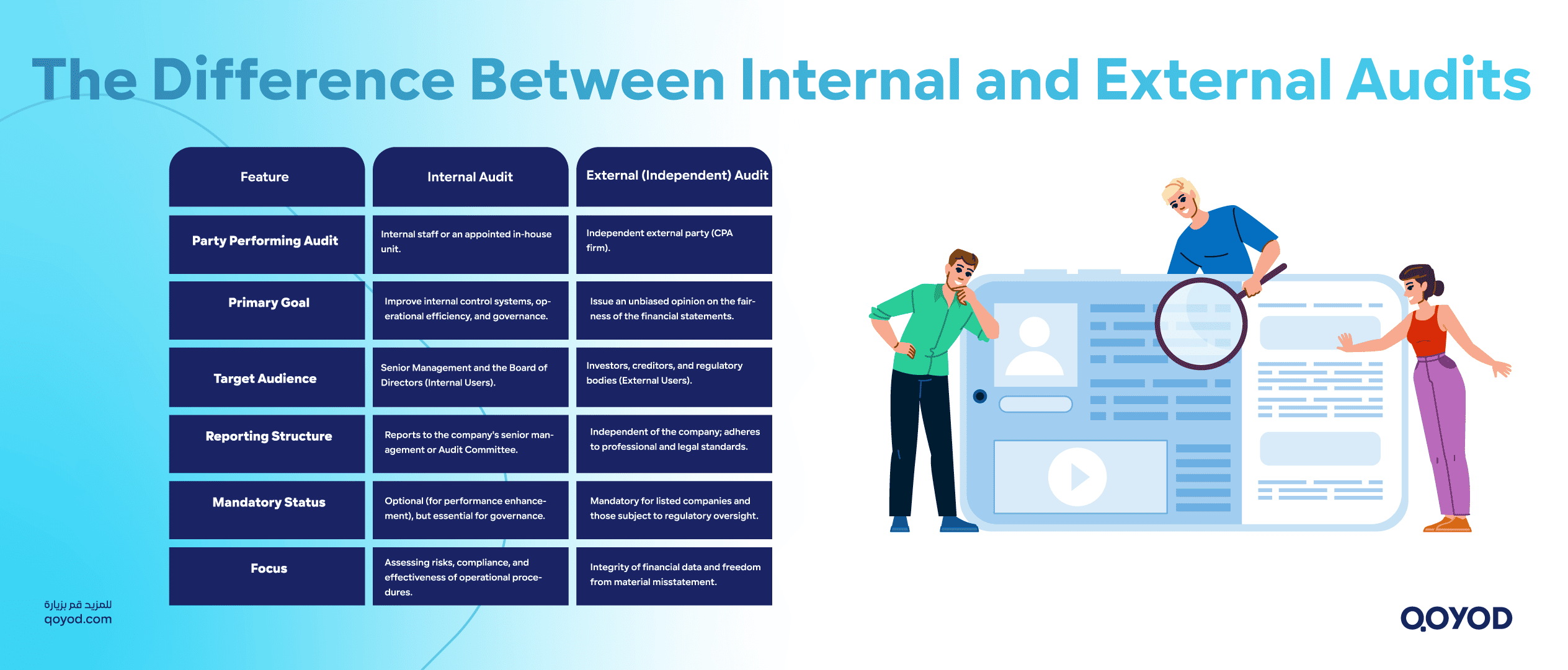
The Difference Between Internal and External Audits
- Internal Audit:
- An in-house activity performed by the company’s internal staff or an appointed internal unit.
- Goal: To examine and improve internal control systems, operational procedures, and corporate governance.
- Scope: Supports management in achieving objectives, mitigating risks, ensuring compliance, and improving operational efficiency.
- Reporting: Typically reports to senior management or the Audit Committee within the company structure.
- External (Independent) Audit:
- A review conducted by an external party (independent Certified Public Accountant – CPA firm) to issue an unbiased opinion on whether the company’s financial statements are presented fairly and are free from material misstatement according to adopted standards.
- Goal: Primarily aimed at external users of financial data (investors, creditors, regulators).
- Requirement: Mandatory for listed companies and often for larger private companies in the Kingdom to satisfy regulatory requirements from the Ministry of Commerce and ZATCA.
Distinguishing Between Financial and Accounting Audits
| Audit Type | Primary Focus | Scope and Objective |
| Financial Audit | Financial Statements (Income Statement, Balance Sheet, Cash Flows). | Verifying that the statements reflect the financial position and performance fairly, within a defined scope. Key for external users and focused on reliability and transparency. |
| Accounting Audit | Accounting Records, Systems, and Controls. | A broader scope that includes checking the integrity of accounting entries, controls, and transaction recording systems. Focuses on the structure of the accounting methodology itself. |
History of Account Audit Evolution in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia has witnessed a fundamental evolution in account audit practices, driven by professional, regulatory, and legislative transformations. This development is crucial for any business, particularly SMBs, to understand the current compliance landscape.
Key Milestones in Saudi Audit Development
- Early Legislative Framework: The establishment of the Saudi Organization for Chartered and Professional Accountants (SOCPA) (formerly SOCPA) as the independent body overseeing the accounting and auditing profession.
The issuance of the CPA System regulates the registration, obligations, and oversight of certified accountants.
- Adoption of International Standards: The Kingdom officially adopted the International Standards on Auditing (ISAs) for mandatory application, ensuring consistency with global best practices.
- Accrual Accounting Transition: The public sector transitioned from cash-basis to accrual-basis accounting, adopting International Public Sector Accounting Standards (IPSAS) to boost financial transparency and accountability, aligning with Saudi Vision 2030 goals.
- Enhancing Professional Quality: Increased focus on quality assurance and oversight of audit firms by regulatory bodies like the Capital Market Authority (CMA) and SOCPA, fostering greater confidence in financial reporting, especially for businesses in financial hubs like Dammam and Khobar.
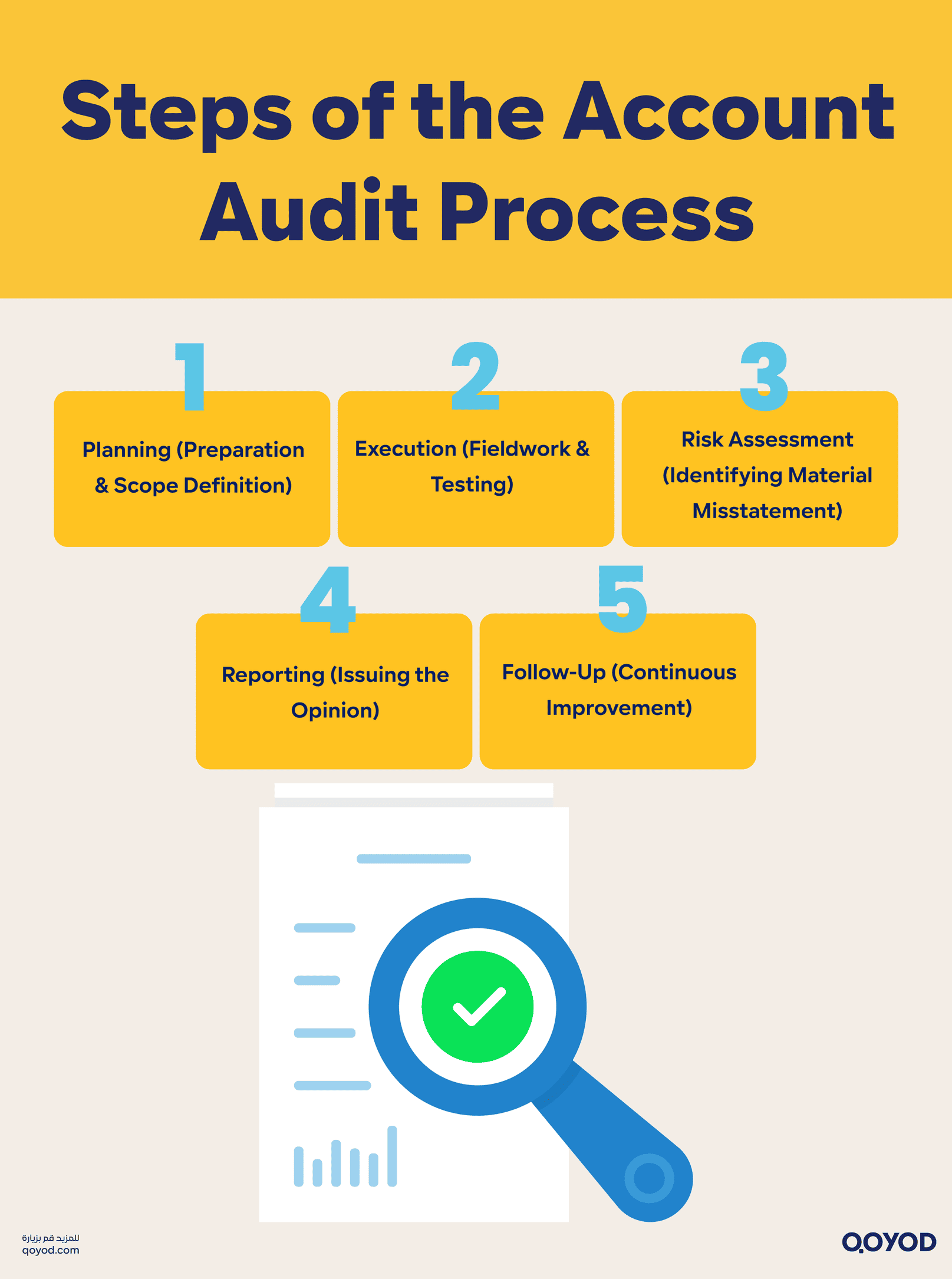
Steps of the Account Audit Process
Executing an account audit is a step-by-step process that reflects the professionalism of the accounting system and quality control. Professional audit firms in the Kingdom must follow a systematic approach covering planning, execution, risk assessment, reporting, and follow-up. Using modern tools like Qoyod Accounting Software significantly streamlines these steps.
1. Planning
The auditor defines the scope, gathers preliminary information about the entity (activity, environment, internal controls, and potential risks). Appropriate audit tools and techniques are selected, such as data analytics and software linkages.
Qoyod’s Role: By providing accurate, electronic accounting records, internal audit trails, and easy extraction of periodic statements, Qoyod provides the auditor with a clean, verifiable starting point, reducing initial preparation time.
2. Execution (Fieldwork)
The auditor examines accounting entries, analyzes transactions, tests internal controls (Control Testing), and performs detailed tests (Substantive Tests) to ensure records match the presented financial statements.
Local Context: Regulated financial entities in Saudi Arabia are required to have an internal audit function and prepare internal control documentation, as mandated by the CMA Governance Regulation.
Qoyod’s Role: Qoyod Accounting Software facilitates the seamless transfer of ledgers and balances, automates report generation, and helps conduct risk analysis using data consistency checks, accelerating execution and reducing manual errors.
3. Risk Assessment
The auditor evaluates the risks of material misstatement due to error or fraud and designs appropriate responses. This assessment forms the basis for the nature and extent of further audit procedures.
Regulatory Compliance: SOCPA-approved standards in Saudi Arabia require auditors to follow a risk-based approach aligned with the International Auditing and Assurance Standards Board (IAASB).
Qoyod’s Role: A modern system like Qoyod can automatically flag deviations or suspicious transactions (e.g., unusual journal entries), allowing the auditor to focus attention on high-risk areas.
4. Reporting
Upon completion of the examination, the auditor issues a professional opinion on whether the financial statements are fairly presented within the adopted standards. The report includes the Opinion (Unmodified, Qualified, Adverse, or Disclaimer), the Basis for Opinion, and any recommendations.
Local Context: SOCPA issues periodic updates on reporting standards, adopting changes to ISAs.
Qoyod’s Role: Companies using Qoyod can easily provide the auditor with prepared financial statements, data links, and review reports, facilitating the timely issuance of the final report and quick response to audit observations.
5. Follow-Up
This phase involves reviewing the implementation of the auditor’s recommendations, addressing internal control weaknesses, and updating the plan for the next audit cycle. This is critical for continuous governance.
Qoyod’s Role: With Qoyod, companies can establish an electronic follow-up log for recommendations, automate alerts for resolving observations, and link actual performance to audit findings, enhancing the corrective cycle’s effectiveness.
Types of Account Audits and Their Objectives
There are several types of audits, each targeting different operational and oversight objectives relevant to the Saudi market.
- Financial Audit (Statutory Audit):
- Focus: Reviewing financial statements for a professional opinion on fair presentation.
- Relevance to KSA: Required for listed companies and large private entities by local laws. Key to ensuring investor trust and meeting regulatory demands.
- Compliance Audit:
- Focus: Checking adherence to relevant laws and regulations such as Value Added Tax (VAT), Zakat regulations, labor laws, or financing contracts.
- Relevance to KSA: Essential for avoiding penalties from ZATCA and ensuring compliance with the mandatory e-invoicing system in Saudi Arabia.
- Information Systems Audit (IT Audit):
- Focus: Examining accounting systems, electronic controls, data security, and transaction processing systems.
- Relevance to KSA: Crucial in the digital era, especially for financial institutions under the purview of the Saudi Central Bank (SAMA) and for companies mandated to use digital record-keeping.
- Operational (Management) Audit:
- Focus: Analyzing the efficiency and effectiveness of operational and managerial processes (e.g., purchasing, inventory, logistics).
- Relevance to KSA: Provides recommendations for improving operational efficiency, such as optimizing inventory costs for a factory in Madinah, boosting overall business value.
Audit Standards and Saudi Legal Requirements
Compliance with local and international audit standards is a fundamental requirement in the Kingdom, vital for promoting trust and transparency.
Key Standards and References
- International Standards on Auditing (ISA): Adopted by SOCPA in Saudi Arabia with local customizations.
- International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS): Mandated for public interest entities (PIEs) and generally for listed entities in the Kingdom.
- Relevant Saudi Laws: Includes the 2021 Law of the Accounting and Auditing Profession, CMA’s Governance Regulations for companies, and SAMA’s internal control and audit regulations.
Importance of Compliance
Compliance for SMBs in the Kingdom is not just a formality; it is essential:
- Investor Confidence: Enhances the belief of investors and stakeholders that the financial statements are true and transparent.
- Reduced Regulatory Risk: Minimizes the risk of fines and penalties, particularly from ZATCA, CMA, or SAMA. Failure to conduct an external audit can delay company registration or license renewal.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies demonstrating high-quality financial reporting and serious internal controls can attract better funding or more stable partnerships, facilitating the goals of Saudi Vision 2030.
- Effective Corporate Governance: Aligns with regulations that mandate an internal audit function and annual plans, reporting to the board of directors.
The Role of Qoyod Accounting Software in Facilitating the Account Audit
Qoyod Accounting Software plays a central role in enhancing data quality, simplifying processes, and reducing the time and cost of the account audit for Saudi SMBs.
Program Features Relevant to the Audit Process
- Accurate and Organized Accounting Record: Qoyod allows for documented entries and attachments (invoices, transfers, agreements) to be uploaded alongside transactions, ensuring high transparency.
- Real-Time Reporting: Provides instant reports such as Income Statements, Balance Sheets, and Trial Balances via the cloud platform, offering auditors immediate access to necessary data.
- Compliance with Saudi Regulations: Qoyod is ZATCA-certified for e-invoicing, fully supporting VAT and other local tax reporting requirements, streamlining compliance audits.
- Strong Internal Controls: Features like customizable cost centers, user access permissions, and transaction workflows enhance internal control effectiveness within the organization.
How Qoyod Helps Companies Pass Audits Smoothly
| Benefit | Description |
| Preparation | Provides readily available accounting data and easily exported reports, drastically reducing the time auditors need to access information. |
| Control Improvement | Enhances internal controls by defining user permissions and maintaining an Audit Trail, making the accounting record more reliable. |
| Reduced Cost | When records are prepared, reports are available, and attachments are linked, the auditor requires less time, potentially lowering audit fees. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Supports compliance, particularly with the mandatory e-invoicing system in Saudi Arabia, minimizing regulatory risks. |
Adopting smart accounting software like Qoyod is a strategic investment for any Riyadh or Dammam business aiming to make the account audit process less burdensome and more value-adding.
Tips for a Smooth and Successful Account Audit Process
To ensure a successful and value-adding account audit, consider these practical tips:
Account Reconciliation Methods
- Prepare and document updated opening balances before the start of the fiscal year.
- Conduct bank reconciliations regularly (at least monthly), comparing bank statements with the bank ledger in your system (e.g., Qoyod).
- Present detailed aging reports for Accounts Receivable and Payable to the auditor.
- Review and compare cost centers and projects to ensure revenues and expenses are recorded in the correct project, aiding the auditor’s performance understanding.
Maintaining Effective Systems and Controls
- Define user permissions in the accounting system (Qoyod) so that each employee only sees what is relevant to their role, boosting internal control and reducing fraud risk.
- Establish clear policies for large/unusual transactions (e.g., dual approval, spending caps, mandatory documentation).
- Maintain a detailed User Activity Log (Audit Trail) to track all modifications or deletions.
- Regularly monitor for sudden changes or unusual transactions (e.g., unexpected expenses) using system analytics to detect early indicators.
Importance of Preparation and Cooperation
- Involve senior management, accounting, internal control, and IT from the start of the audit planning.
- Provide the auditor with required documentation in advance: chart of accounts, internal policies, previous reports, invoices, financing contracts, etc.
- Organize an opening meeting to clarify the scope, timelines, and available resources.
- Ensure the accounting team is ready and prepared to answer the auditor’s questions.
- Ensure financial statements are closed (finalized) before the auditor’s arrival.
The Role of Account Audits in Boosting Investor and Partner Trust
The benefits of an account audit extend beyond technical compliance to build internal and external trust in the company.
- Investors and Capital Owners: An independent auditor’s opinion signifies a commitment to transparency and accountability, reducing investment risk and increasing investment appeal for SMBs seeking funding.
- Partners and Lenders: They often request audited reports to ensure funds are managed wisely and that accounting data is sound.
- Regulatory Bodies: Authorities like CMA and SAMA highly value audits as a part of governance, and compliance enhances a company’s reputation and funding ability.
- Competitive Advantage: In line with Saudi Vision 2030’s shift toward a knowledge and governance-based economy, companies committed to account audit are seen as trusted players, offering a competitive edge.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about the Account Audit Process
In this section, you will find answers to the most common questions regarding the procedures and processes of account auditing in Saudi Arabia. We clarify official requirements and the latest regulatory standards to help business owners and managers understand the audit process and ensure their companies’ compliance with Saudi regulations
What is the difference between internal and external audit in Saudi Arabia?
Internal audit is performed by a team within the company to assess and improve internal controls, procedures, and operational processes, helping to raise efficiency and reduce risks. External audit, on the other hand, is conducted by an independent accredited entity and aims to review and verify financial data, ensuring its accuracy, transparency, and compliance with SOCPA standards and local regulations. External audits are typically mandatory for large institutions and publicly listed companies in the Saudi financial market.
What is an account audit and why is it important for Saudi businesses?
An account audit is a thorough review of financial records to ensure their accuracy and adherence to Saudi and international standards. Audits boost transparency and trust among investors and regulatory authorities.
What is the difference between internal and external audit?
Internal audit is carried out within the company and focuses on process improvement, while external audit is performed by a third party to confirm the integrity of financial records and their compliance with official standards.
What are the steps of the account audit process in Saudi Arabia?
The steps include planning, information gathering, risk assessment, actual fieldwork, report issuance, and follow-up, as required by the Saudi Organization for Certified Public Accountants (SOCPA).
What are the SOCPA standards for account audits?
SOCPA standards establish the overall framework for audit procedures, covering transparency, uniformity of standards, and accuracy of financial reports. Saudi companies are required to comply fully with them.
Is external audit mandatory for all companies?
External audit is mandatory for listed joint-stock companies and is also required by some government entities for financial institutions. Some smaller companies may be exempt depending on their size and activity.
How do I choose an accredited audit firm in Saudi Arabia?
Ensure the firm is licensed by SOCPA, has practical experience in your business field, and enjoys a strong professional reputation in the Saudi market.
What are the penalties for non-compliance or financial misconduct discovered during audits?
Penalties vary from fines and license suspension to permanent company closure, depending on the type, severity, and recurrence of the violation.
How does an accounting solution (like Qoyod) help streamline the audit process?
It organizes financial records, provides easy data access, and offers detailed reports, enabling auditors to review accounts faster and more accurately.
What are the latest developments in international audit standards adopted in Saudi Arabia?
Key advancements include the implementation of risk-based methodologies, enhanced digital analysis tools, and integration of financial reports with the Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority platform.
Conclusion: Making the Audit a Strength with Qoyod
The account audit is not just a formal or mandatory activity; it is a fundamental pillar of modern financial management and a strategic lever for a company’s transparency, reliability, and market standing. By adopting rigorous audit standards, enhancing internal controls, and utilizing advanced accounting software, companies can transform the review process from a burden into a source of strength.
We encourage every business in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia from SMBs to large enterprises—to embrace auditing as an integral part of their financial management system and to invest in appropriate technologies, such as Qoyod Accounting Software.
Try Qoyod Accounting Software now to make your business operations easier and more accurate with solutions designed for Saudi companies.
Don’t hesitate to visit our website today and start developing your invoicing system through our e-invoicing workshops for compliance and professionalism with Qoyod, ensuring your business runs smoothly and expertly. You can benefit from the 14-day free trial now.