In the fast-paced business world of Saudi Arabia, managing Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable is fundamental to accurately tracking financial obligations and entitlements. These core accounting concepts require professional management to ensure your business’s financial stability and continuity, especially for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) navigating the E-invoicing system and Zakat regulations.
Accounts Payable (AP) represents the company’s financial liabilities that must be settled on time, while Accounts Receivable (AR) signifies the funds owed to the company by its customers. Effective management goes beyond simple recording; it involves analysis and active administration to support business liquidity and facilitate sound financial decisions across cities like Riyadh, Jeddah, and Dammam.
Facing increasing challenges, Qoyod Accounting Software provides an advanced program fully compliant with local Saudi laws and accounting standards. Qoyod is designed to help you manage your Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable with ease and efficiency. It allows you to track invoices, monitor due dates, and generate crucial financial reports, enhancing your overall financial performance.
Join us as we explore the key differences, critical importance, and best practices for managing these accounts to enhance your company’s cash flow. Discover how Qoyod is the complete solution for businesses in Saudi Arabia.
Understanding Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable
A deep understanding and effective management of Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable are essential pillars for any institution’s financial health. These central accounts represent the company’s obligations and entitlements to external parties, directly impacting its ability to maintain financial liquidity and ensure smooth, effective operations.
The importance of efficient management lies in its vital role in balancing financial liabilities with cash entitlements. This positively influences cash flow, increases profitability, and strengthens trust with both suppliers and customers. This comprehensive guide will define AP and AR, explain their accounting entries, and highlight the fundamental differences to help you manage your financial accounts with high efficiency.
What is a Purchase Order and Why is it Important?
1. What is Accounts Payable (AP)?
Accounts Payable refers to the monetary amounts owed by the institution to its suppliers or creditors for goods or services received without immediate payment. AP is classified as a current liability on the balance sheet, representing obligations that the institution must settle by their due dates.
Examples of Accounts Payable (AP) in Saudi Arabia:
- Invoices for raw material purchases from suppliers in Khobar.
- Amounts due for essential services like electricity or internet.
- Short-term loans from local Saudi banks.
Accounting Entries for Accounts Payable (AP):
Recording AP usually starts with a journal entry upon receipt of the statement:
| Transaction | Debit | Credit |
| Purchase of goods on credit | Inventory / Purchases | Accounts Payable – Suppliers |
| Payment to Suppliers | Accounts Payable – Suppliers | Cash / Bank |
2. What is Accounts Receivable (AR)?
Accounts Receivable refers to the monetary amounts owed to the institution by its customers or other parties for goods or services sold without immediate cash collection. AR is listed under current assets on the balance sheet and is a primary source of liquidity for any business, including those in Madinah.
Examples of Accounts Receivable (AR) in Saudi Arabia:
- Credit sales invoices issued to customers.
- Entitlements resulting from deferred-payment service delivery.
- Short-term loans granted to customers.
Accounting Entries for Accounts Receivable (AR):
AR is typically recorded as follows:
| Transaction | Debit | Credit |
| Sale of goods or services on credit | Accounts Receivable – Customers | Sales Revenue |
| Receipt of cash from customers | Cash / Bank | Accounts Receivable – Customers |
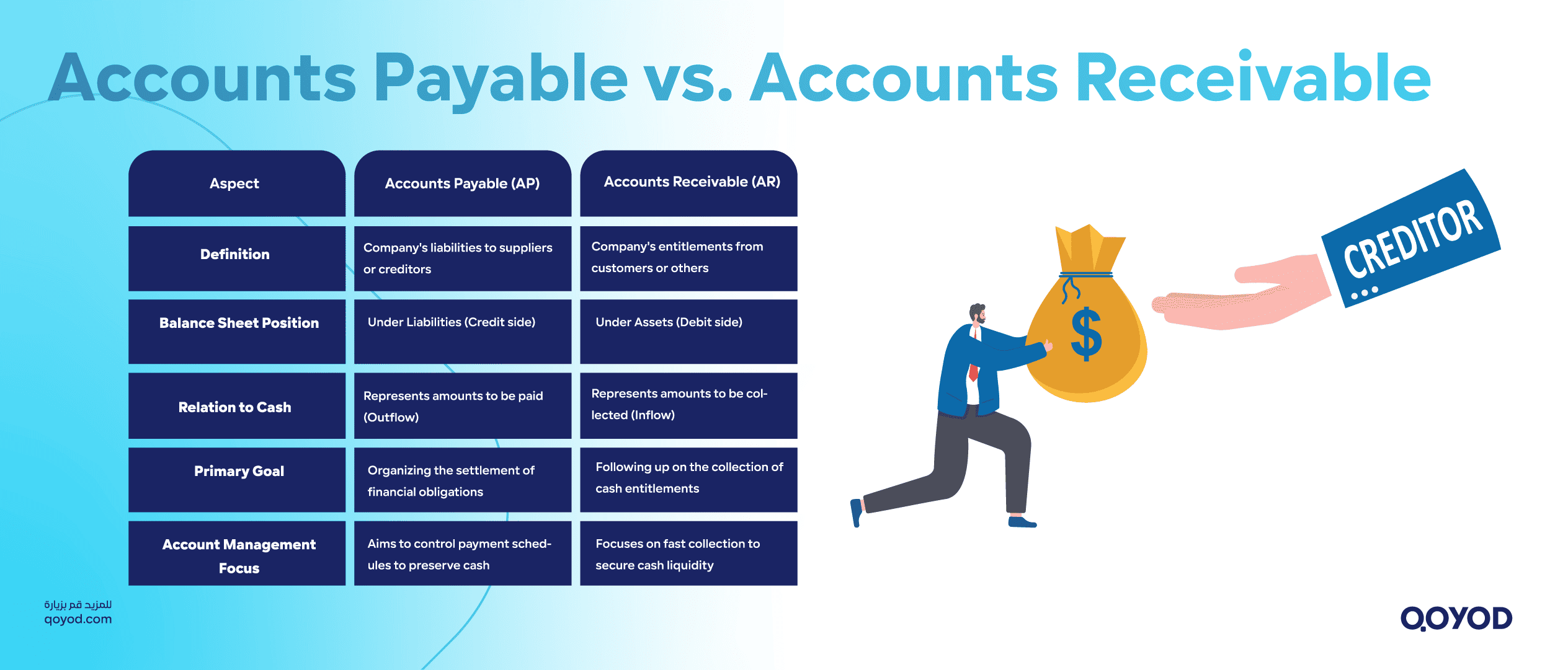
Key Differences Between Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable
| Aspect | Accounts Payable (AP) | Accounts Receivable (AR) |
| Definition | Company’s liabilities to suppliers/creditors | Company’s entitlements from customers/others |
| Balance Sheet Location | Liabilities (Credit side) | Assets (Debit side) |
| Cash Relationship | Represents amounts to be paid | Represents amounts to be collected |
| Main Goal | Managing timely settlement of financial obligations | Monitoring timely collection of cash entitlements |
| Account Management | Focuses on controlling payment schedules to preserve cash | Focuses on rapid collection to secure liquidity |
The accurate understanding and effective management of both Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable allow your Saudi institution to control its financial resources and obligations. This supports healthy commercial relationships and enhances the company’s rational financial planning capability.
We will now cover how to analyze these accounts, important performance indicators, and best practices for improving financial account management using Qoyod Accounting Software.
Impact of Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratios
The turnover ratio for Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable is a vital financial indicator that reflects the efficiency of a company’s management of its due and owed accounts. This ratio shows the number of times the company converts Accounts Receivable into cash during a specific period or how quickly it pays its Accounts Payable to suppliers.
- High AR Turnover suggests the company has strict credit policies and receives payments quickly. This improves cash flow and ensures the necessary liquidity for new projects and expansion. However, a very high turnover might indicate overly restrictive credit terms, limiting market opportunities.
- AP Turnover indicates how quickly the company settles its dues to suppliers. A high turnover reflects financial discipline, but it could limit opportunities to use cash efficiently for operational financing. A low turnover might suggest an expansion of credit periods or potential cash flow problems.
Analyzing and Evaluating AP and AR in Saudi Institutions
| Practical Steps | Role of Modern Accounting Systems (Qoyod) |
| Data Collection | Provides accurate financial data on AP and AR automatically. |
| Ratio Calculation | Calculates turnover rates, collection periods, and payment periods automatically. |
| Performance Comparison | Compares performance against industry averages or previous periods to identify strengths and weaknesses. |
| Customer/Supplier Evaluation | Evaluates customer and supplier adherence to payment terms to sustain business or renegotiate credit terms. |
| Regular Follow-up | Monitors collection and payment consistently to take early action on delayed payments. |
Modern accounting systems, like Qoyod Accounting Software, provide advanced capabilities for automated tracking and analysis of accounts:
- Automatic Monitoring: Tracks Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable invoices with automatic alerts for due dates.
- Advanced Reporting: Generates rotational reports illustrating AP/AR turnover, and collection/payment periods.
- Decision Support: Analyzes trends and provides recommendations to improve liquidity and cash flow.
- ZATCA Compliance: Full integration with the Saudi E-invoicing system ensures compliance with the Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority (ZATCA) regulations.
By utilizing these tools, Saudi SMEs can manage their accounts more efficiently, mitigating the risks of delayed collection or payment, thereby enhancing long-term financial health and profitability.
Qoyod’s Role in Efficiently Managing Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable
The accurate management of Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable is a cornerstone for maintaining a company’s financial balance. Best accounting software in Saudi Arabia, Qoyod, emerges as a comprehensive solution empowering institutions to manage these accounts with high efficiency and accuracy.
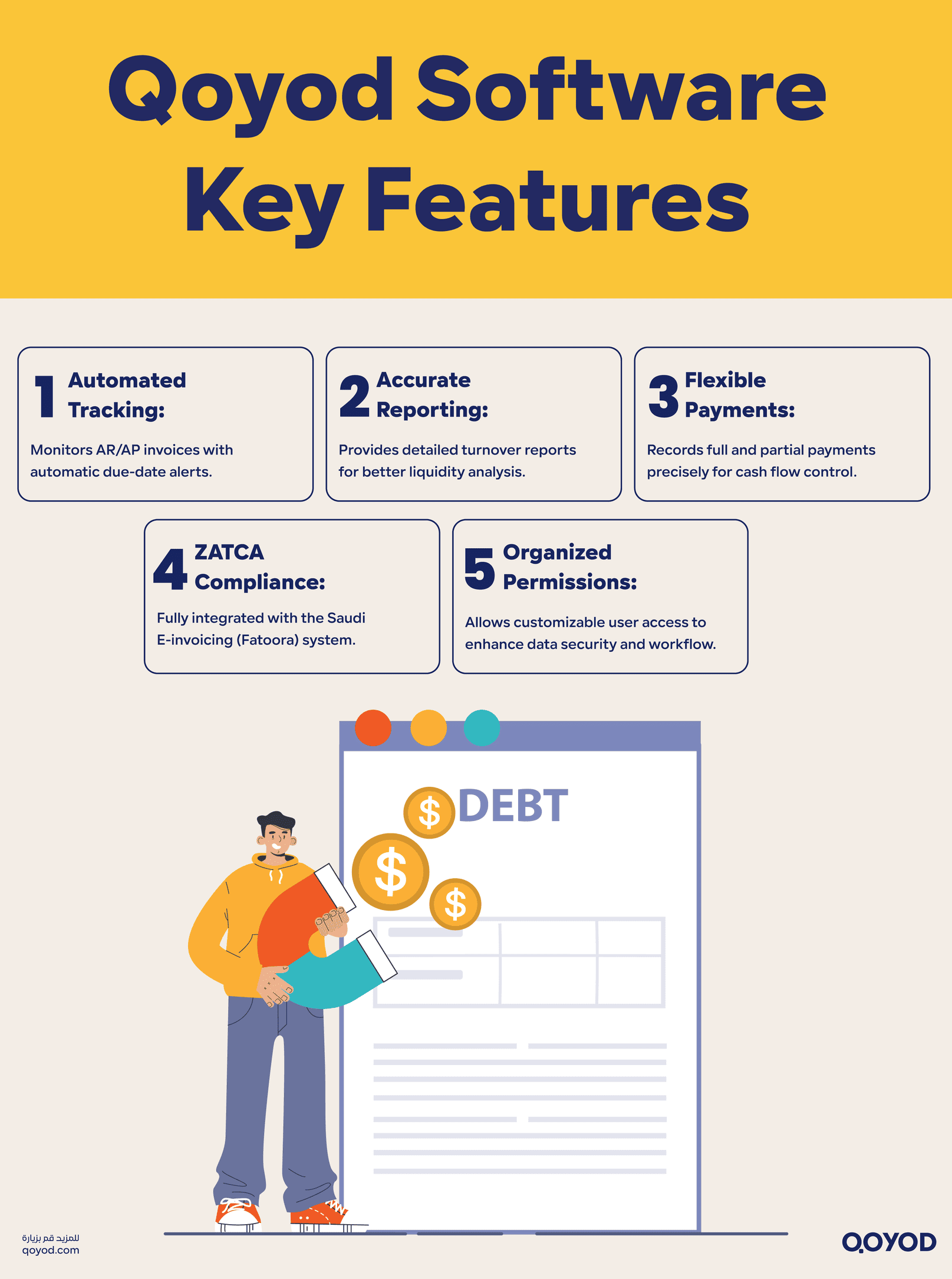
Practical Features of Qoyod Software
- Automated Invoice Tracking: Qoyod automatically tracks both AR and AP invoices with due-date alerts, minimizing delays in collection or settlement.
- Advanced Rotational Reports: Provides comprehensive, specialized reports on turnover rates and collection/payment periods, aiding financial analysis and informed decision-making.
- Multiple Payment Management: Allows the recording of full or partial payments for accounts with customizable dates and logs, increasing the accuracy of cash flow monitoring.
- E-invoicing System Integration: Fully supports integration with the E-invoicing system (Fatoora) mandated by ZATCA, ensuring compliance with Saudi government regulations.
- Coordinated User Permissions: Enables various staff permissions to maintain data security and organize workflow, crucial for businesses in major economic hubs like Riyadh and Jeddah.
Example Application for Saudi SMEs:
A trading company operating in Dammam uses Qoyod to manage thousands of Accounts Payable invoices from multiple suppliers. The Accounts Manager receives automatic alerts for upcoming due dates, accurately tracking payments for each invoice without losses.
A services institution uses Qoyod in Madinah to record credit sales to customers. It effectively monitors the due dates of its Accounts Receivable and manages collections via detailed reports, significantly reducing overdue invoices.
For more on the Best Accounting Software in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Practical Tips for Better Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable Management
| Collection and Payment Strategies | Avoiding Financial Risks |
| Regular Review: Periodically review AP/AR lists, classify high-risk accounts, and take early action. | No Ignoring Overdue Accounts: Establish a clear and proactive collection plan for late payments. |
| Incentives: Offer incentives for early customer payment and negotiate flexible payment terms with suppliers to boost cash flow. | Credit Review: Regularly review customer creditworthiness and update policies based on their payment performance. |
| Early Warning: Utilize early warning systems and send automated reminders before payment due dates. | Departmental Coordination: Ensure close coordination between Finance and Sales departments to mitigate AR-related risks. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable
What is the difference between accounts payable and accounts receivable?
Accounts payable are a company's obligations to others (usually suppliers), while accounts receivable are the rights a company has to claim money from others (usually customers).
How do accounts payable and receivable appear on the balance sheet?
Accounts payable are listed under current liabilities, whereas accounts receivable are classified as current assets.
Why is managing accounts payable and receivable important for companies?
Effective management ensures financial liquidity, helps control cash flow, and reduces the financial risks associated with late payments or defaults.
What does the turnover ratio for accounts payable and receivable mean?
The turnover ratio is a financial metric that measures how efficiently a company collects its receivables or pays its payables within a certain period.
What are the recommended steps if a customer defaults on their receivables?
It is advised to communicate with the customer, arrange a new payment schedule, or use legal services to collect the debt if necessary.
Are receivables always considered current assets?
Yes, because they are expected to be collected within a short period (usually less than a year).
What risks are associated with accounts receivable?
The main risks are non-collection or delayed payment, which can negatively affect liquidity and cash flow.
How does artificial intelligence contribute to managing payables and receivables?
AI assists through predictive analysis, automating reminders and invoicing, and early detection of financial risks with customers or obligations.
Can payment terms in accounts payable be negotiated?
Yes, many suppliers allow negotiation of payment periods or offer early payment discounts according to company policy.
How are accounting entries for payables and receivables recorded?
Payables are recorded as liabilities on the credit side, while receivables are recorded as assets on the debit side of the accounting entry.
Conclusion
Accurate management of Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable is the foundation for controlling financial performance and achieving stability and growth for your business in Saudi Arabia. Accounting solutions for Riyadh businesses and nationwide, Qoyod Accounting Software, with its advanced features and integration with ZATCA systems, helps you enhance the monitoring of your due accounts and ensure healthy financial liquidity.
Make Qoyod your strategic partner today on your journey toward more efficient and effective financial management to achieve your institutional goals with confidence and transparency.
Try Qoyod Accounting Software now to make your business operations easier and more accurate with solutions designed for Saudi companies.