| (Excerpt) :
The Revenue Recognition principle is vital for Saudi SMEs to accurately reflect financial performance and ensure compliance with ZATCA and the e-invoicing system in Saudi Arabia. This guide, tailored for the Saudi market, explains how proper recognition (per IFRS 15) records revenue only upon fulfilling actual obligations, which is crucial for profit analysis and cash flow. Simplify this critical process and maintain compliance using tailored Qoyod Accounting Software solutions. |
For any small or medium-sized business (SME) doing business in Saudi Arabia, the revenue recognition concept is essential. Do your current accounting procedures fairly represent the financial success of your business, especially in light of Saudi Arabia’s mandated e-invoicing system and Zakat compliance?
Whether your company is based in Riyadh, Jeddah, or Dammam, it is imperative that your financial reports be transparent, reliable, and compliant in an economy that is quickly modernizing under Vision 2030.
This thorough manual explores the significance of the Revenue Recognition concept and is specifically designed for the Saudi audience. We’ll describe how it maintains compliance with local laws (ZATCA) and international standards (IFRS 15), increases investor confidence, and guarantees that revenues are only recorded when genuine economic responsibilities are met. Knowing this is essential for precise cash flow management and profit analysis, which are made much easier with a customized solution like Qoyod Accounting Software.
How Revenue Recognition Benefits Investors and Regulators by Improving Transparency and Ensuring Financial Data Integrity
The accounting principle known as revenue recognition requires a company to record the value of revenue as realized only after a significant economic event, such as the completion of services for a client or the transfer of ownership of products, has taken place. This depends on the revenue being consistently quantifiable and the likelihood of receiving the related payment in the future.
Key Points:
- Revenue isn’t recognized simply upon signing contracts or sending invoices; it’s recognized when the primary contractual obligations (like delivery or service performance) are completed.
- The value of the revenue must be clearly defined, with the business genuinely entitled to the monetary compensation for the performance rendered.
Importance of Revenue Recognition in Accounting
For a number of reasons, the revenue recognition concept is essential, particularly when it comes to accounting solutions for Riyadh businesses:
- Accurate Financial Picture: It guarantees that the financial performance accurately depicts not only the time of cash receipts but also the period in which revenues were earned.
- Transparency and Credibility: It upholds strict standards for financial reports and avoids results inflation by early recognition of unearned earnings.
- Comparability: Because the timing and revenue computation are transparent and based on recognized standards such as US GAAP (ASC 606) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS 15), it facilitates the comparison of financial performance across various time periods and businesses.
- Reliability: It supports the reliability of financial statements for investors, analysts, and regulatory bodies (like ZATCA), mitigating risks of financial manipulation and adhering to the Matching Principle (pairing revenues with their corresponding expenses).
Compliance with the Revenue Recognition principle reflects sound governance and forms the basis for informed economic decisions by management and financial statement users alike.
Impact of Revenue Recognition on Cash Flow and Profitability Analysis
Revenue Recognition has a direct and crucial impact on a company’s cash flow and profitability analysis, serving as a primary determinant of the financial data’s credibility and realism.
Impact on Cash Flow
The actual receipt of cash does not necessarily correspond with the recognition of income. Even if payment hasn’t been received yet, a business can record revenue as soon as it satisfies its commitment to the client (such as delivery or service provision).
- The company’s actual cash flow is made clearer by this division between accounting recognition and actual cash collection.
- It keeps cash assets from inflating unnecessarily, which is frequently the result of relying on credit sales.
- Good revenue rules make it easier to analyze operating cash flows realistically, which enables investors and management in Jeddah or Khobar to evaluate the company’s capacity to make money from its main business rather than just book profits.
Impact on Analysis of Profitability
The key component in calculating the accounting profit for a given period is revenue recognition.
- According to the Matching Principle (matching revenues with expenses), recording only realized revenues results in a net profit figure that accurately represents the performance of the business.
- It serves as the foundation for precisely computing financial measures like return on equity and earnings per share as well as for comparing profitability over time.
- Assessing future profitability is also impacted by proper revenue recognition, particularly for businesses with long-term contracts. Revenue recognition based on completion phases keeps results from inflating and guarantees the accuracy of financial data prior to market and regulatory inspection.
Proper Revenue Recognition policies ensure transparent cash flows and credible profitability analysis, empowering the company to achieve superior financial management and make precise decisions.
Learn More: What are cash flow statements, and what are their types?
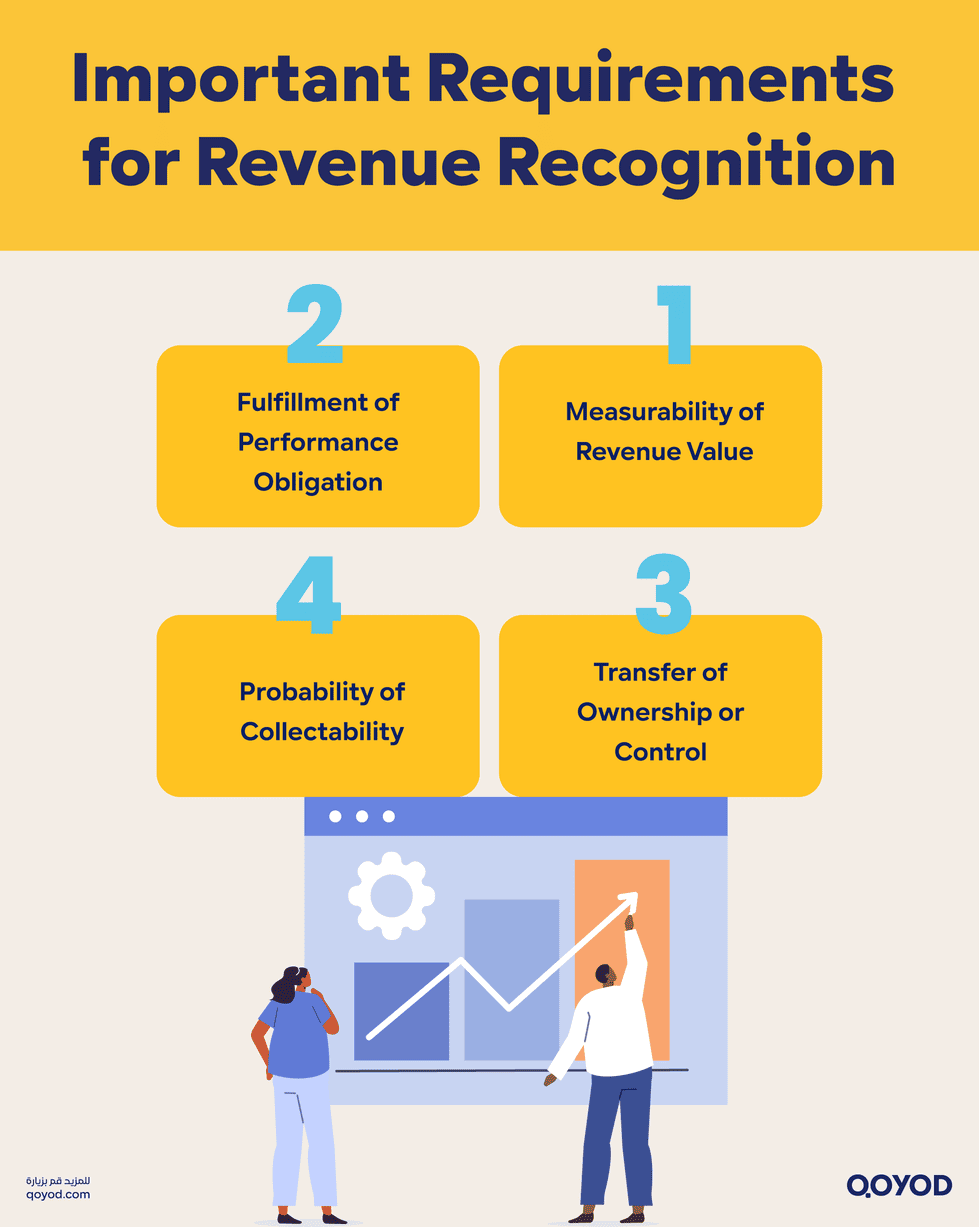
Important Requirements for Revenue Recognition
Revenue isn’t just randomly acknowledged. It must meet a number of strict requirements to guarantee the accuracy of financial statements and adherence to ASC 606 and IFRS 15.
1. Meeting Performance Requirements
- Revenue is recorded only when the business completes its obligation to the customer; that is, after delivering the goods or rendering the service specified in the contract.
- The revenue is recognized when the actual activity that creates the company’s right to receive payment has been achieved (e.g., product delivery or service performance).
2. Measurability
- The revenue’s value needs to be precisely and consistently quantifiable. The selling price or service value must be decided without ambiguity or subjective guesswork, and it must be obvious and certain from the contract date.
- This requirement improves openness and shields financial statements from erroneous projections. Utilize Qoyod Accounting Software to measure your revenue precisely.
3. Probability of Collectability
- The customer’s ability to pay the revenue amount shouldn’t be seriously questioned. Before recognizing the revenue, the business must have a reasonable level of confidence in the client’s capacity to send the required amount.
- Recognition must be delayed until the risks of non-collection are reduced or the money is collected if there are significant risks of non-collection (such as an untrustworthy client).
4. Transfer of Ownership or Control
- Only when ownership of the items or control over the service is transferred to the client is revenue recognized.
- Control refers to the customer’s ability to guide the use of the product and reap its benefits while assuming the risks and rewards that come with it. Depending on the circumstances, the transfer may take place just after delivery or after the service is over.
Applying Revenue Recognition to Long-Term Projects (e.g., Contracting in Dammam)
Revenue recognition in long-term contracting projects, which are typical in Dammam and Madinah, involves more than just collecting agreements or prepayments. Because projects create revenues and expenses gradually dependent on work progress, it takes unique procedures to ensure that revenues represent the actual performance during each accounting period.
| Method | Description | Use Case & Impact |
| Percentage of Completion (PoC) | Revenue and costs are recognized proportional to the percentage of work completed out of the total project. | Preferred under IFRS 15. Shows actual performance per period. Calculation methods: cost-to-cost, effort expended, or actual work performed. |
| Completed Contract Method | Revenue and costs are recognized only after the contract is entirely finished and delivered. | Used for short projects or when progress/cost is hard to reliably estimate. May distort financial performance during the project’s execution period. |
Methods for Revenue Recognition in ContractingAccounting Challenges in Contracting
- Determining Percentage of Completion: Difficulties in accurately assessing progress impact the reliability and integrity of revenue data.
- Cost Estimation: Changes in the expected project costs necessitate adjustments to recognized revenues and loss provisions.
- Anticipated Losses: Obligatory creation of a loss provision if expected costs exceed expected revenues.
The Role of IFRS 15 (Five-Step Model)
A five-step approach is required by the international standard IFRS 15 to determine when and how businesses recognize revenue:
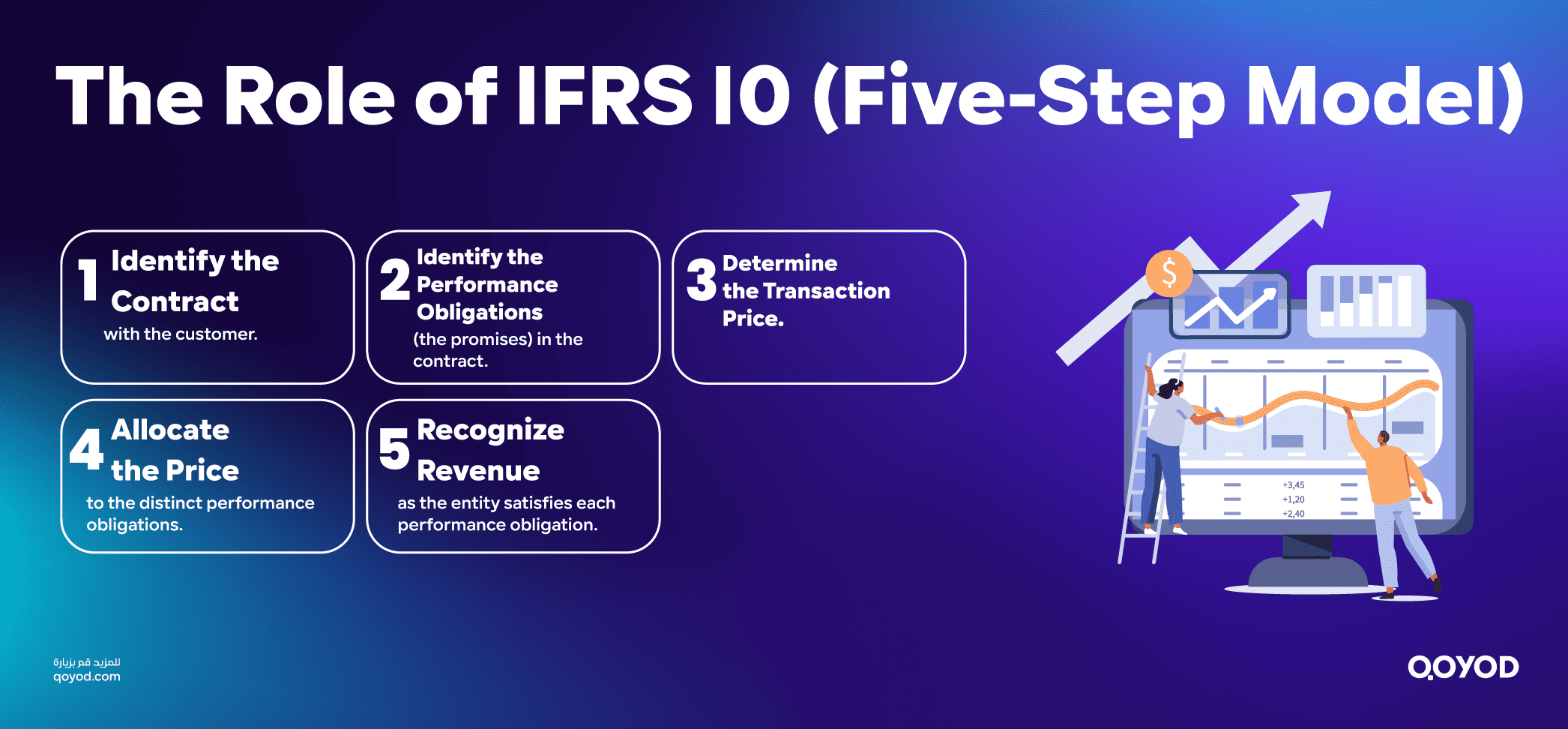
- Determine which contracts you have with the client.
- Determine each of the contract’s distinct performance requirements.
- Establish the price of the transaction.
- Assign the performance obligations the transaction price.
- Revenue is recognized as soon as the organization fulfills a performance obligation.
IFRS 15 particularly encourages the Percentage of Completion method for long-term projects with reliable progress measurement to ensure accurate and fair revenue recognition over the project’s duration.
Accrued vs. Unearned Revenue (Prepaid Income)
Understanding the difference is fundamental for accurate financial statements for small businesses in Saudi Arabia.
| Component | Accrued Revenue (Earned Revenue) | Unearned Revenue (Prepaid Income) |
| Definition | Revenue realized by actually providing goods or services to the customer. | Money received in advance for goods or services not yet delivered or performed. |
| Recognition Time | Upon delivery of goods or performance of the service. | Upon receipt of cash before providing the good or service. |
| Impact on Income Statement | Recorded as Revenue in the Income Statement during the period earned. | Does not appear in the Income Statement; recorded as a Liability on the Balance Sheet. |
| Impact on Balance Sheet | Appears as an Asset (e.g., Accounts Receivable) if cash is not yet received. | Appears as a Liability because the company owes the service/product. |
Practical Example: Annual Subscription Service
A software company in Riyadh receives the full sum up advance when it offers a yearly membership for SAR 1,200. The service must be rendered over a 12-month period by the company.
- Using the Revenue Recognition Principle: The entire SAR 1,200 is not recognized by the business in the month of collection. Rather, it is dispersed during the duration of the subscription.
- Recognition each month: SAR 100 is recorded as Earned Revenue at the end of every month. The remaining remains a liability known as unearned revenue.
This example demonstrates how gradual recognition reflects the company’s actual performance and is tied to the stages of service delivery, not just the timing of cash collection.
Conclusion: Driving Trust with Qoyod
Correct and measured Revenue Recognition actively contributes to enhancing the transparency, integrity, and credibility of financial reports. This dramatically boosts the confidence of investors, stakeholders, and regulatory bodies (like ZATCA) in the presented financial data.
For small and medium-sized businesses in Saudi Arabia, mastering this principle is not just about compliance with IFRS 15; it’s about making smarter business decisions, ensuring accurate Zakat calculations, and navigating the complexities of the e-invoicing system in Saudi Arabia.
Try Qoyod Accounting Software now to make your business operations easier and more accurate with solutions designed for Saudi companies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is Revenue Recognition?
It is the principle of determining the correct time to record revenues in accounting books when specific criteria are met, such as the transfer of benefit or service to the customer.
When is Revenue Recognized in Accounting?
Revenue is recognized upon fulfilling the accounting standard's conditions, such as substantial completion of the service, delivery of goods, transfer of risks, and a high probability of collecting the sales value.
What is the difference between Earned (Realized) Revenue and Unearned (Prepaid) Revenue?
Earned Revenue is for goods or services actually provided and deserved by the company. Unearned Revenue is collected before service/delivery and remains a liability until execution is complete.
How does IFRS 15 Recognize Revenue?
IFRS 15 follows five core steps: identifying the contract, identifying performance obligations, determining the transaction price, allocating the price, and recognizing revenue upon satisfying each obligation.
What are the steps of Revenue Recognition?
The steps include: having a clear customer contract, identifying performance obligations, knowing the selling price, allocating the price among obligations, and finally recognizing revenue upon fulfilling each obligation.
Examples of Revenue Recognition in Contracting Companies?
In contracting, revenue is often recognized based on the percentage of completion, recognizing revenue gradually as work is completed over the contract period, not in one lump sum.
Examples of Revenue Recognition in Software Companies?
Software companies recognize revenue upon product delivery or based on monthly cloud service subscriptions, considering the time period the customer receives the benefit.
Does Revenue Recognition differ by Business Type?
Yes, policies vary. For instance, service companies record revenue upon service delivery, while installment sales companies may record it with each installment or upon delivery, as per the contract.
What is the impact of Revenue Recognition on Profits and Cash Flow?
Correct recognition directly impacts profitability and cash flows, helping present an accurate financial picture for better investment, financing, or tax decisions.
How is Revenue Recognized in Installment Sales Contracts?
Revenue is typically recognized when the ownership of the good is transferred, with each installment recorded as a subsequent collection. Revenue may be recognized with each payment if there's a continuous performance obligation.
How do Contract Modifications Affect Revenue Recognition?
Modifications require re-evaluating the performance obligations and transaction price, and fairly allocating the price to the new obligations, which may delay or accelerate revenue recognition in some cases.